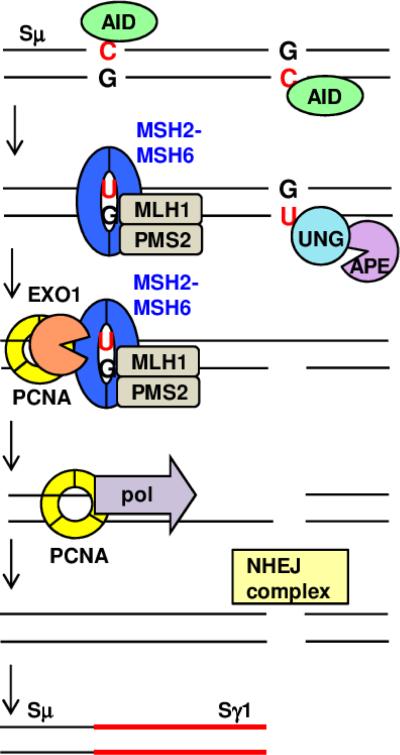
Fig. 2. MMR proteins assist in the conversion of BER-induced single-strand nicks to double-strand break substrates for CSR.
AID-induced uracils in immunoglobulin switch region DNA can be bound by either BER or MMR proteins. In BER, UNG and APE remove the uracil and create a single-strand nick. MMR proteins MSH2-MSH6 and MLH1-PMS2 encounter a uracil on the opposite strand and attract EXO1 and PCNA to an adjacent nick. EXO1 excises the sequence between the nicks, leading to a 5’ overhang that is processed by PCNA and a translesion polymerase to create a blunt double-strand break. Alternatively, the overhang can be deleted by EXO1 or a 5’ flap endonuclease. An analogous process can occur with MMR proteins acting on a uracil located 3’ to the BER-induced nick (not shown). When double-strand breaks occur simultaneously in different switch regions, recombination produces a new switch junction mediated by NHEJ factors, as illustrated here between Sμ and Sγ1.