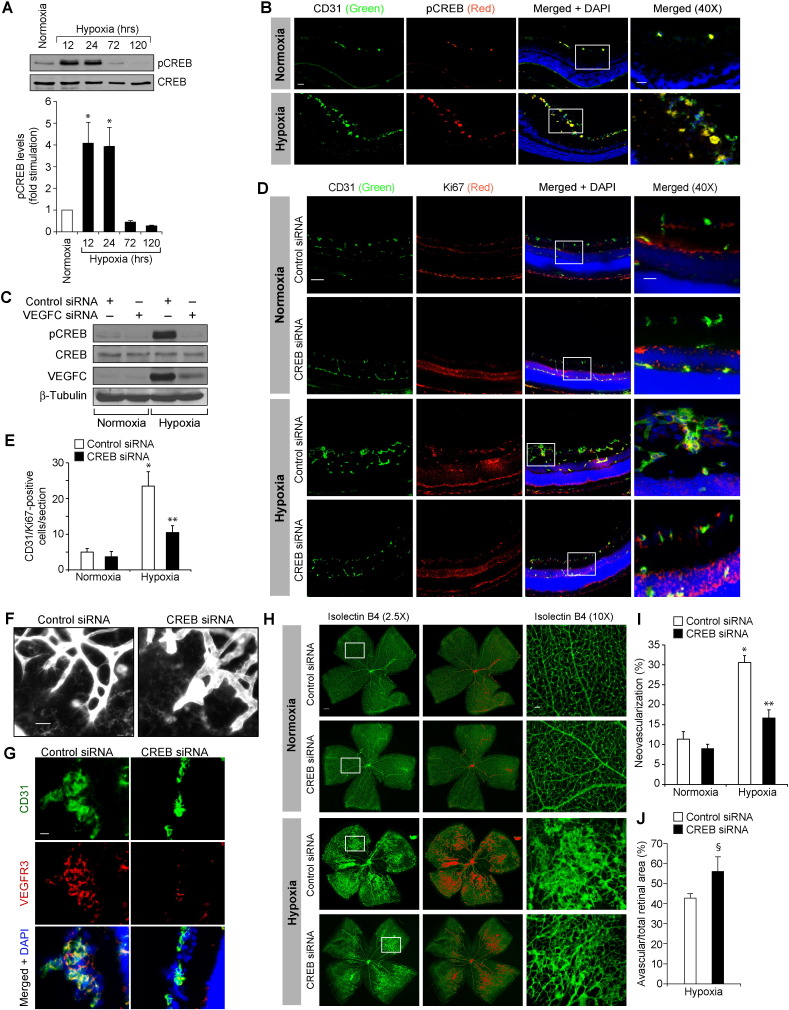
Fig. 3.
CREB mediates hypoxia-induced retinal neovascularization. A. An equal amount of protein from normoxic and various time periods of hypoxic retinal extracts were analyzed by Western blotting for pCREB levels using its phospho-specific antibody and normalized to CREB. B. Following exposure to hyperoxia from P7 to P12, pups were returned to room air and at P15 the retinas were isolated, fixed, cross-sections were made and stained by immunofluorescence for CD31 and pCREB. C. All the conditions were the same as in panel B except that pups were administered intravitreally with 1 μg/0.5 μl/eye of control or VEGFC siRNA at P10 and P11 and at P13 the retinas were isolated and tissue extracts were prepared. An equal amount of protein from normoxic and hypoxic retinal extracts was analyzed by Western blotting for pCREB and CREB levels as described in panel A and the blot was reprobed for VEGFC or β-tubulin levels to show the effects of the siRNA on its target and off-target molecules, respectively. D. All the conditions were the same as in panel C except that pups were administered intravitreally with 1 μg/0.5 μl/eye of control or VEGFC siRNA at P12 and P13 and that at P15 the retinas were isolated and processed for CD31 and Ki67 immunofluorescence staining as described in Fig. 2, panel A. The right column shows the higher magnification (40 ×) of the areas selected by rectangular boxes in the images shown in the left column. E. Retinal EC proliferation was measured by counting CD31- and Ki67-positive cells that extended anterior to the inner limiting membrane per section (n = 6 eyes, 3 sections/eye). F. All the conditions were the same as in panel D except that control or CREB siRNAs were injected intravitreally at P12, P13, and P15 and at P17 the retinas were isolated, stained with isolectin B4, flat mounts were made and examined for EC filopodia formation at 40 × magnification. G. All the conditions were the same as in panel D except that the sections were stained for CD31, VEGFR3 and DAPI. H. All the conditions were the same as in panel F except that retinal neovascularization was measured at 2.5 × magnification. Retinal vascularization is shown in the first column. Neovascularization is highlighted in red in the second column. The third row shows the selected rectangular areas of the images shown in the first column under 10 × magnification. I & J. Retinal neovascularization (I) and avascular areas (J) were determined as described in “Materials and Methods.” The bar graphs represent quantitative analysis of three blots or 6 retinas. The values are presented as Mean ± SD. * p < 0.01 vs normoxia or normoxia + control siRNA; ** p < 0.01 vs hypoxia + control siRNA; § p < 0.05 vs hypoxia + control siRNA. Scale bar represents 50 μm and 20 μm in panels B & D, far left column and far right column, respectively, 20 μm in panels F & G, 300 μm and 50 μm in panel H, far left column and far right column, respectively.