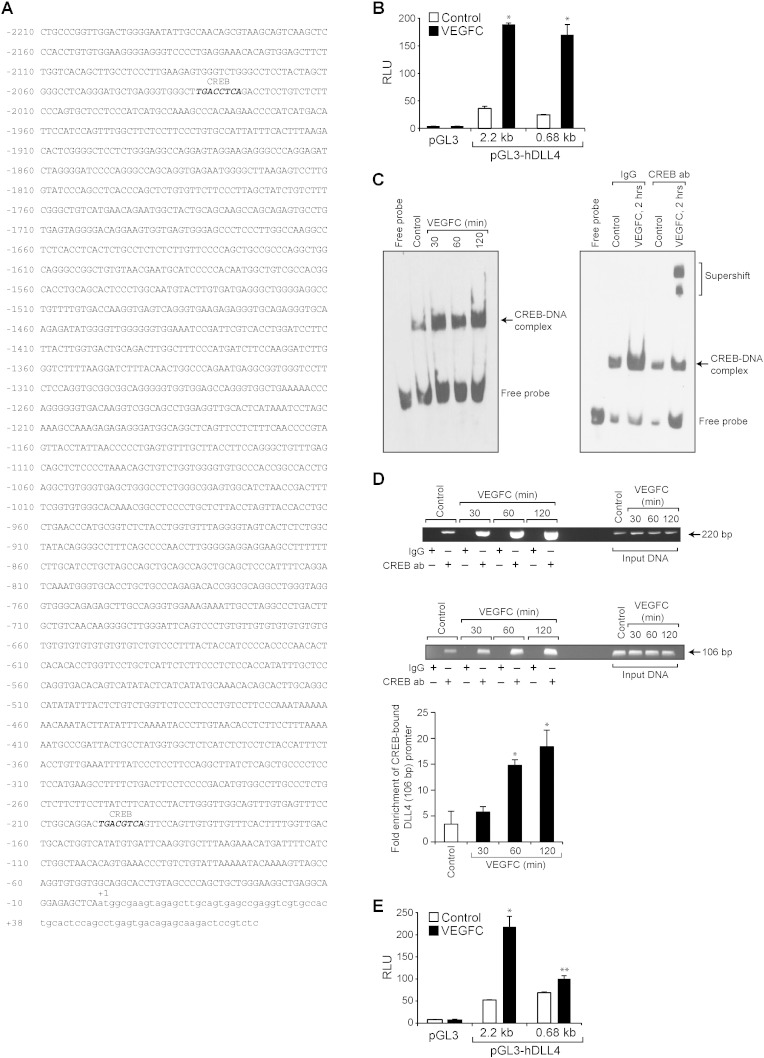
Fig. 5.
CREB is required for VEGFC-induced DLL4 promoter activity. A. DLL4 promoter encompassing − 2210 nt to + 78 nt was cloned and the nucleotide sequence with CREB binding sites highlighted in bold italic letters is shown. B. The full-length (from − 2210 nt to + 78 nt) and a truncated DLL4 promoter encompassing from − 605 nt to + 78 nt were sub-cloned into pGL3 vector yielding pGL3-hDLL4 (2.28 kb) and pGL3-hDLL4 (0.68 kb) plasmids. HRMVECs were transfected with empty vector or pGL3-hDLL4 (2.28 kb) or pGL3-hDLL4 (0.68 kb) promoter plasmid DNAs, growth-arrested, treated with vehicle or VEGFC for 4 h and the luciferase activity was measured. C. Left panel: Nuclear extracts of control and various time periods of VEGFC (100 ng/ml)-treated cells were analyzed by EMSA for CREB binding using CREB-binding site at − 193 nt as a Biotin-labeled probe. Right panel: Nuclear extracts of control and 2 h of VEGFC (100 ng/ml)-treated cells were analyzed by supershift EMSA using normal IgG or anti-CREB antibodies. D. Control and various time periods of VEGFC (100 ng/ml)-treated cells were analyzed for CREB binding to DLL4 promoter by ChIP assay using two sets of primers that amplify a 220 bp and a 106 bp DNA fragments surrounding the CREB-binding site at − 193 nt. The data in the bar graph in panel D represents the qPCR of 106 bp region of CREB-bound DLL4 promoter. E. HRMVECs were transfected with empty vector or pGL3-hDLL4 (0.68 kb) promoter plasmid DNA with and without the CREB-binding site mutated (TGA was mutated to CTC), growth-arrested, treated with and without VEGFC (100 ng/ml) for 4 h and the luciferase activity was measured. The bar graphs represent quantitative analysis of three independent experiments. The values represent Mean ± SD. * p < 0.01 vs control; ** p < 0.01 vs pGL3-hDLL4 (0.68 kb) + VEGFC.