Figure 3.
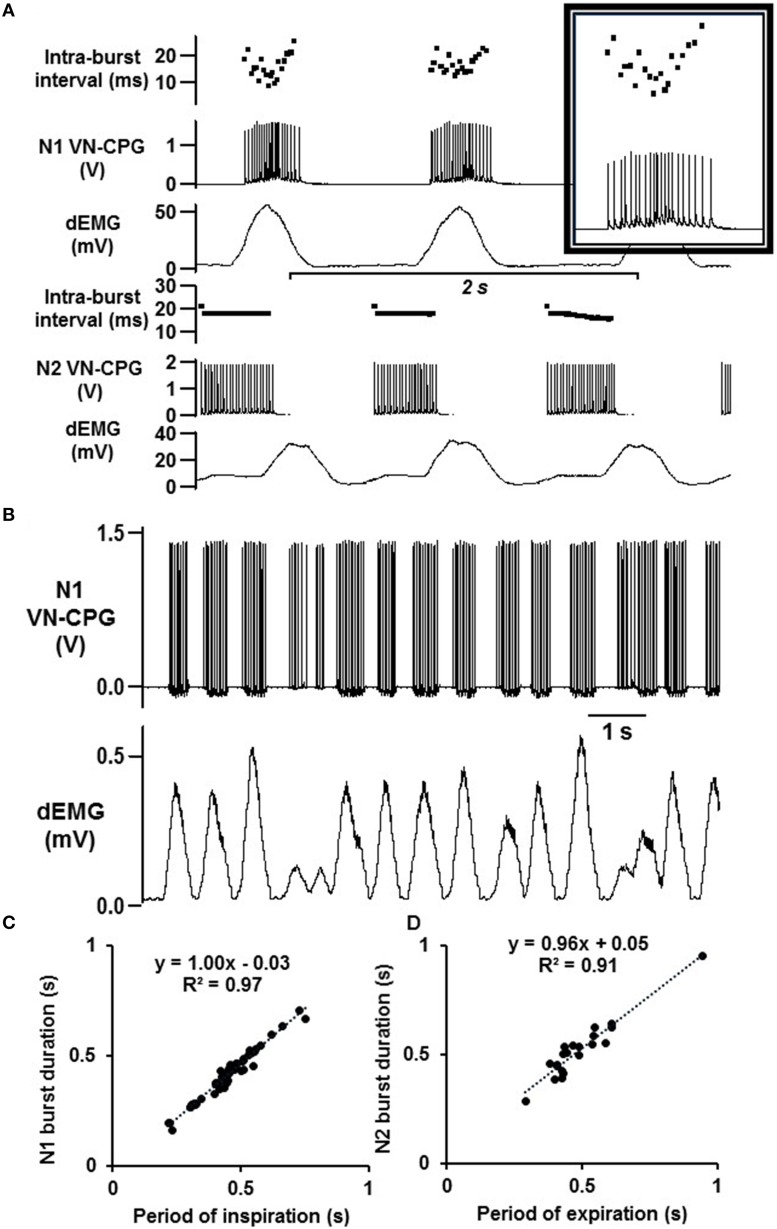
Instantaneous VN-CPG processing enables biological feedback. (A) The amplitude and intra-burst interval of the VN-CPG N1 mimics the dEMG input signal, where the N1 amplitude and intra-burst interval (inset) fluctuate with the height of the dEMG amplitude. N2 is inhibited when N1 activity reaches a threshold and therefore exhibits a constant amplitude and intra-burst interval during the expiratory period. The timing of N1 bursts instantaneously adapts to spontaneous changes in breathing (B). The duration of N1 (C) and N2 (D) are directly related to the periods of inspiration and expiration respectively. The slope of the linear regression for N1 is 1.00 (R2 = 0.97), indicating the instantaneous processing of dEMG input and conversion into N1 stimulus output to precisely coincide with inspiration. dEMG, diaphragm electromyogram; VN-CPG, hCPG for vagal nerve stimulation.