Fig. 3.
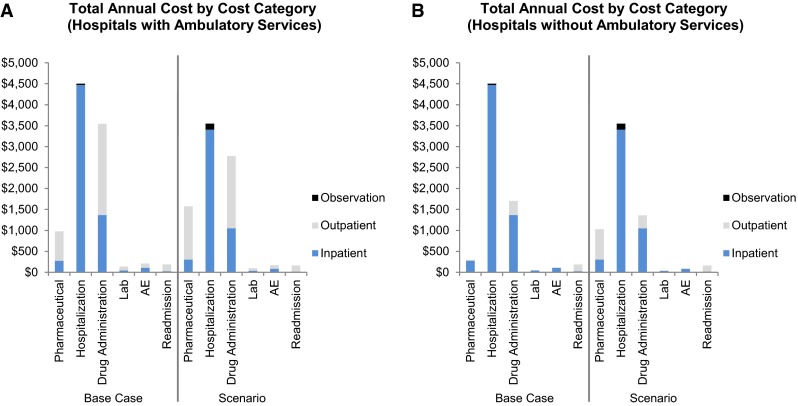
Total annual cost by cost category for a US hospital with 1000 acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection patients receiving intravenous MRSA-active antibacterials: a total annual cost by cost category for hospitals with ambulatory services; and b total annual cost by cost category for hospitals without ambulatory services. For the base case and scenario, pharmaceutical represents the drug acquisition costs only for all antibacterials included in the model; hospitalization is the cost of inpatient stay excluding costs associated with pharmaceuticals, drug administration, laboratory tests, and monitoring associated with MRSA-active antibacterials included in the model, adverse events, and readmissions; drug administration is the costs associated with drug administration, excluding pharmaceutical acquisition costs; lab is the costs of laboratory tests and monitoring associated with MRSA-active antibacterials included in the model; AE is the cost associated with the adverse events listed in Table 1; and readmission represents the costs associated with 30-day re-hospitalization. AE adverse event, MRSA methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
