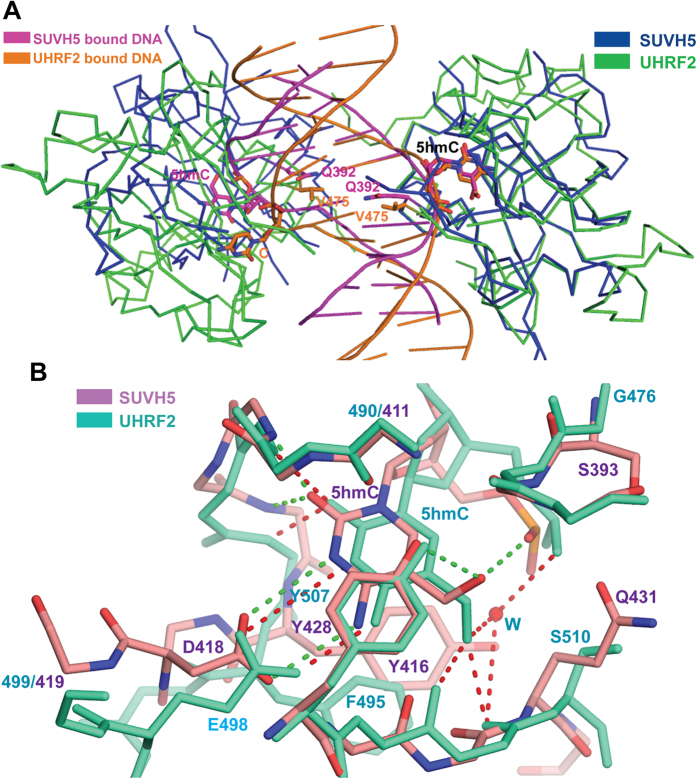
Figure 4. Structural comparison between the SRA domains of SUVH5 and UHRF2, showing the dual flip out and 5 hmC recognition.
(A) Superposition of the complexes containing the SUVH5 SRA (blue ribbon) bound to the fully-5 hmCG DNA (magenta cartoon) onto UHRF2 SRA (green ribbon) bound to the hemi-5 hmCG DNA (orange cartoon). The SRA domains on the right are superimposed to allow the visualization of the relative displacement and orientation of the SRA domains on the left. (B) Superposition of the flipped-out 5 hmCs in the SUVH5 SRA (5 hmC and the binding pocket residues are shown as orange in atomic color) and UHRF2 SRA (5 hmC and the binding pocket residues are shown in greenish cyan) complexes within their respective binding pockets. The 5 hmC-mediated network of interactions with the binding pocket residues of SUVH5 SRA and UHRF2 SRA are depicted as dashed lines in green and red, respectively. A bridging water molecule is involved in the inter- and intramolecular recognition of the OH group of 5 hmC in UHRF2 SRA and is shown as a red sphere.