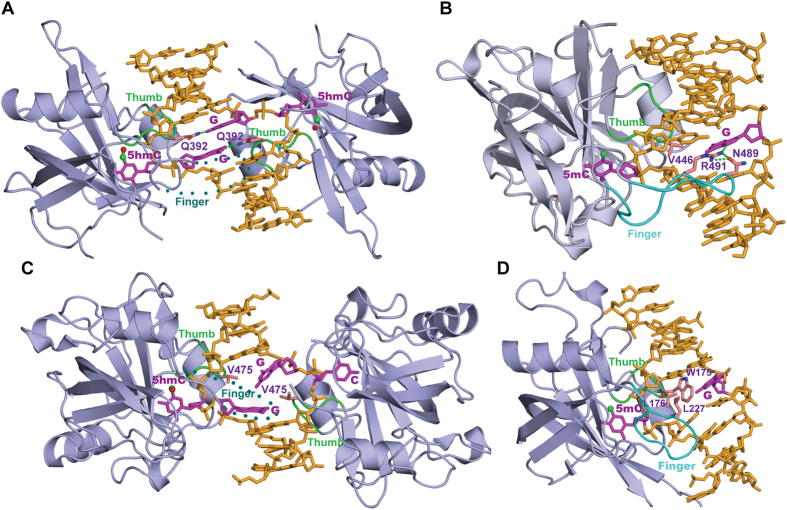
Figure 5. Structural comparison between the SRA domains of SUVH5, UHRF1, UHRF2 and SUVH4 bound to the fully-5 hmCG, hemi-5 mCG, hemi-5 hmCG and hemi-5 mCHG duplex DNA.
(A) Structure of the 2:1 SUVH5 SRA-fully-5 hmCG DNA duplex complex. Note the dual flip-out of the symmetrical 5 hmCs from adjacent base pairs on the partner strands. The thumb loop, which is involved in 5 hmC flipping, and the disordered finger segment are shown in green and dotted cyan, respectively. For clarity, only the finger loop from the left SRA is indicated. (B) Structure of the 1:1 UHRF1 SRA-hemi-5 mCG DNA duplex complex, where only 5 mC is flipped out from the duplex DNA (PDB: 3CL2) and is recognized by the single SRA domain. Two loops, finger and thumb, are shown in green and cyan, respectively. The residues on the finger loop partially fill the hole left by the flipped out 5 mC base, and functions by interacting with the orphaned G and could shield the unmodified C from being recognized by the second SRA domain. (C) Crystal structure of the 2 UHRF2 SRA domains bound to a hemi-5 hmCG DNA (PDB: 4PW6). 5 hmC and C are flipped out from adjacent base pairs on the partner strands and are positioned in the binding pockets of the individual SRA domains. The mode of recognition is similar to SUVH5 SRA bound to fully-5 hmCG. The thumb and disordered finger loops are indicated as described for the structure of the SUVH5-fully-5 hmCG complex shown in Fig. 5A. (D) Structure of an SUVH4 SRA domain bound to the hemi-5 mCHG duplex DNA (PDB: 4QEP). Only 5 mC is flipped out from the duplex DNA and is positioned in the SRA binding pocket. The thumb and finger loops are indicated as described for the structure of the UHRF1-hemi-5 mCG complex. Both the thumb and finger loops, which are involved in base flipping, interrogate the 5 mCHG duplex DNA through minor and major grooves, respectively. Leucine residues from the thumb and finger loops fill the holes left by the flipped out 5 mC and are involved in van der Waals interactions within the duplex DNA.