Figure 7. Interactions among AMF, neighbor plants and target plants for phytoremediation under Pb stress conditions.
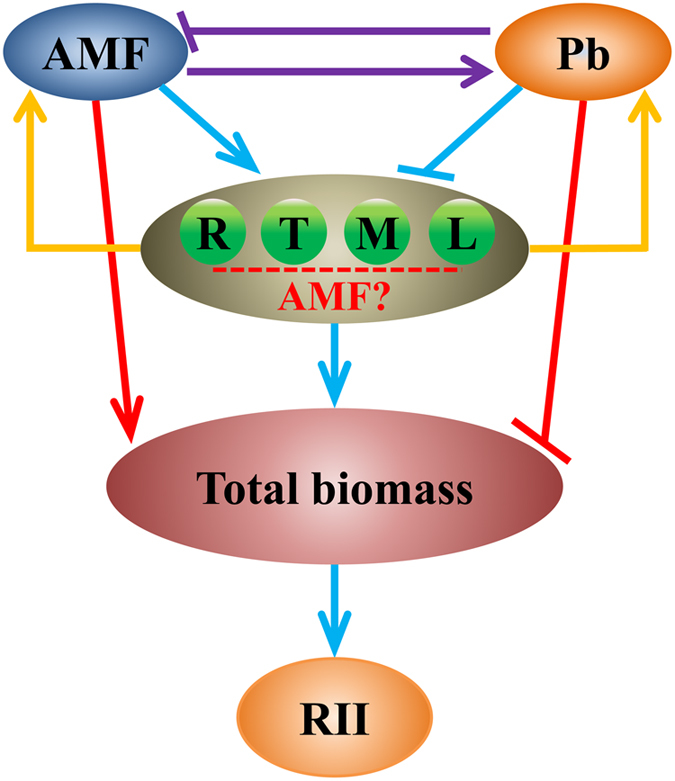
The potential roles of AMF in phytoremediation and tree-herb interactions in Pb contaminated soil. Purple arrows ( ): high Pb level inhibits the MC of plants except for L. perenne (L), while AMF inoculation significantly increases the root Pb concentration, but decreases the shoot Pb concentration of all plants at the highest Pb level (1500 mg kg−1 Pb); Yellow arrows (
): high Pb level inhibits the MC of plants except for L. perenne (L), while AMF inoculation significantly increases the root Pb concentration, but decreases the shoot Pb concentration of all plants at the highest Pb level (1500 mg kg−1 Pb); Yellow arrows ( ): legume and grass neighbors increase and decrease the MC of co-cultured plants, respectively. In addition, legume neighbors improve the Pb accumulation in both shoots and roots of co-cultured plants via reducing soil pH; Red arrows (
): legume and grass neighbors increase and decrease the MC of co-cultured plants, respectively. In addition, legume neighbors improve the Pb accumulation in both shoots and roots of co-cultured plants via reducing soil pH; Red arrows ( ): AMF inoculation and Pb addition have positive and negative effects on plant biomass, respectively, and thereby affect the RII and plant completion through a direct pathway; Blue arrows (
): AMF inoculation and Pb addition have positive and negative effects on plant biomass, respectively, and thereby affect the RII and plant completion through a direct pathway; Blue arrows ( ): AMF inoculation and Pb addition influence plant photosynthetic parameters, N, P, S and Mg acquisition and allocation. Some of these factors are related to the biomass of plants as shown in Tables S14 and S15. Therefore, AMF can affect RII and plant completion through an indirect pathway. Red dashed line (
): AMF inoculation and Pb addition influence plant photosynthetic parameters, N, P, S and Mg acquisition and allocation. Some of these factors are related to the biomass of plants as shown in Tables S14 and S15. Therefore, AMF can affect RII and plant completion through an indirect pathway. Red dashed line ( ): the difference effects of AMF on plant interactions between legume-legume and legume-grass are hypothesized to be resulted from various mycorrhizal dependencies among plants.
): the difference effects of AMF on plant interactions between legume-legume and legume-grass are hypothesized to be resulted from various mycorrhizal dependencies among plants.
