Fig. 1.
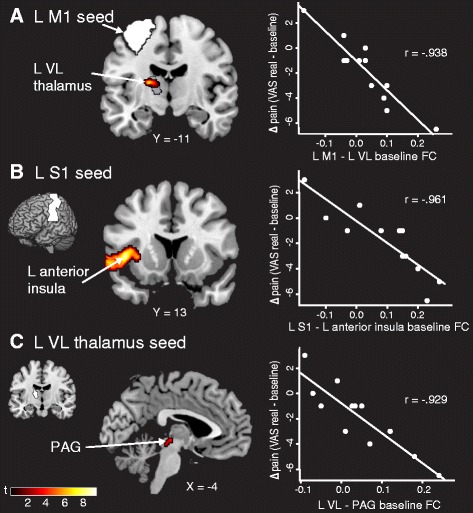
Stronger FC at baseline predicts analgesia. a Patients with higher L M1 (seed in white) − L VL (anatomical region outlined in black) connectivity at baseline had a greater reduction in clinical pain across sham and real transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) periods (displayed at p = 0.005). b Stronger L S1 (seed in white) − L anterior insula FC at baseline predicted a better clinical response. c Connectivity between the L VL thalamus (seed in white) and the PAG at baseline also predicted patients who would respond to sham and real tDCS treatment. Data shown are Fisher-transformed r values. M1 primary motor cortex, VL ventral lateral, S1 primary somatosensory cortex, PAG periaqueductal gray, VAS visual analogue scale, L left, R right, FC functional connectivity
