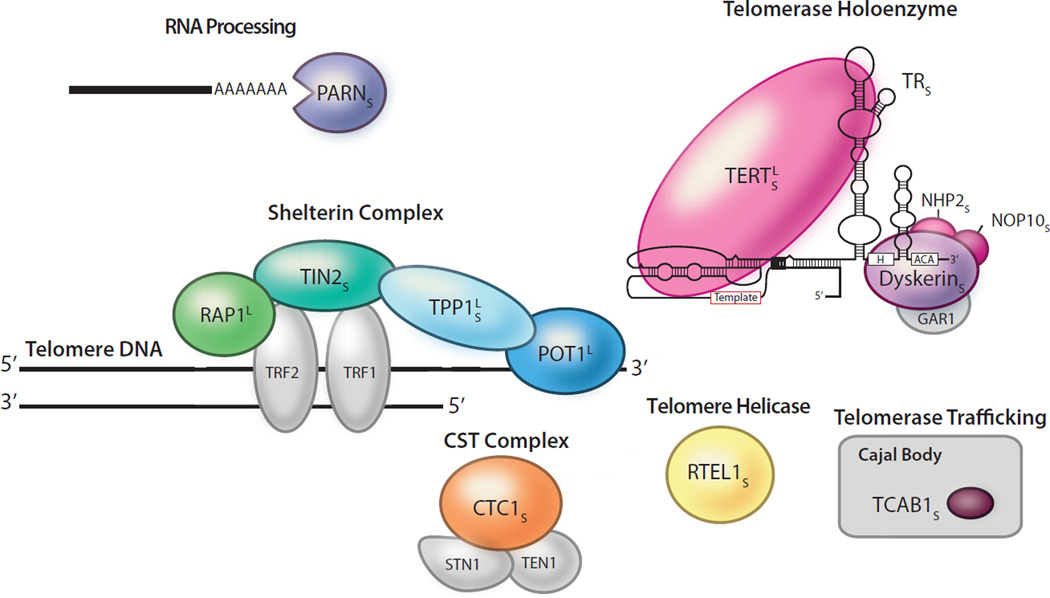
Figure 2. Telomerase and telomere components mutated in both short and long telomere syndromes.
The ‘S’ subscript indicates a link to short telomere syndromes (n = 11 genes), while the ‘L’ superscript indicates a link to long telomere syndromes (n = 4 genes). Mutant components are shown in color and gray denotes telomere components not known to be linked to disease. These mutations affect telomerase catalytic activity or processivity (TERT and TR), telomerase biogenesis (dyskerin encoded by DKC1), NOP10 and NHP2, or telomerase trafficking (TCAB1 also known as WRAP53). Mutations in telomere syndromes may also fall in the shelterin components: TIN2 (encoded by TINF2), TPP1 (encoded by ACD), POT1, or RAP1 (encoded by TERF2IP). CTC1 and RTEL1 affect lagging strand synthesis and telomere replication, respectively. PARN is involved in RNA processing and deadenylation.