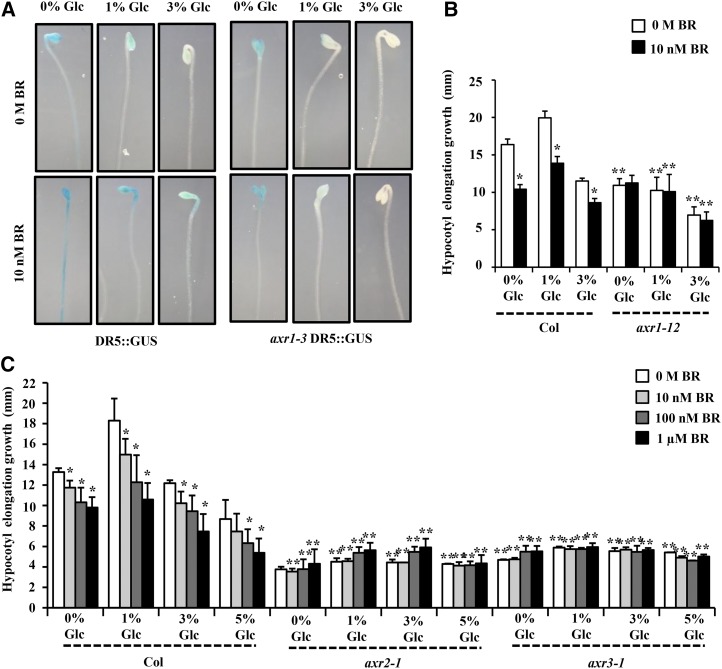
Figure 10.
Involvement of auxin-signaling components in Glc-BR regulation of hypocotyl elongation in etiolated seedlings. A, The BR induction of DR5::GUS expression was inhibited in axr1-3 mutation background. Also, in axr1-3 mutant background, even lower concentrations of Glc were able to inhibit the DR5::GUS expression, suggesting the involvement of AXR1-mediated mechanisms for BR-Glc cross talk. B and C, Quantification of hypocotyl elongation growth in the 7-d-old etiolated wild type (Col-0) and auxin-signaling mutants axr1-12, axr2-1, and axr3-1 seedlings growing on one-half-strength MS medium supplemented with independent as well as combined treatments of Glc and BR in the dark. The auxin-signaling mutant axr1-12 seedlings were found to have significantly reduced sensitivity, whereas axr2-1 and axr3-1 mutants were found highly resistant for different concentrations of Glc and BR for regulation of etiolated hypocotyl elongation growth compared with the wild type. These results indicate the dependence of both BR and Glc action upon these auxin-signaling components for regulation of etiolated hypocotyl growth. Values represent the average from two independent biological replicates, each having at least 15 seedlings (except for axr1-12; data from two biological replicates, 10 seedlings each), and error bars represent se (Student’s t test, P < 0.001; *, control versus treatment; and **, wild type versus mutant).