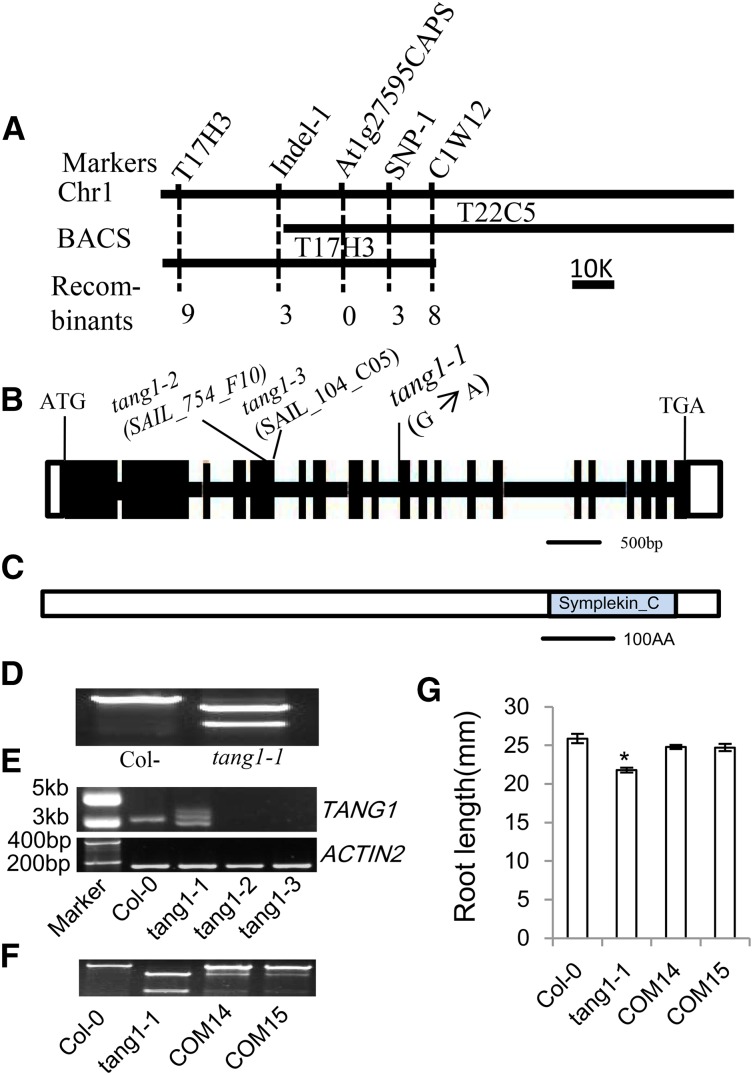
Figure 2.
Map-based cloning of the TANG1 gene. A, Fine-mapping of TANG1. The TANG1 gene was mapped to a 26.5-kb interval between markers Indel-28379 and SNP-54834 and cosegregated with the marker At1g27595CAPS. Recombinant numbers are shown at bottom from F2 plants. BACS, Bacterial artificial chromosome clones. B, Structure of the TANG1 gene. The start codon (ATG) and the stop codon (TGA) are indicated. Black boxes represent exons, and the lines between boxes are introns. The positions of transferred DNA (T-DNA) insertion lines and the point mutation are also indicated. C, The predicted TANG1 protein contains the Symplekin tight-junction protein C-terminal domain. AA, Amino acids. D, The mutation in the tang1-1 allele produces a HindIII site that is used for generating the At1g27595CAPS marker. E, RT-PCR analysis of TANG1 expression in tang1-1, tang1-2, and tang1-3 alleles using the primer pair TANG1CDS FB1+RB2. The first strand cDNAs were prepared from 20-d-old seedlings. The ACTIN2 gene was used as a reference for relative mRNA levels. F, Background identification of Col-0, tang1-1, complementation line 14 (COM14), and COM15 using the At1g27595CAPS marker. COM14 and COM15 were tang1-1 transformed with the wild-type TANG1 genomic sequence. G, Root lengths of 14-d-old seedlings of Col-0, tang1-1, COM14, and COM15. *, P < 0.05 compared with Col-0 (one-way ANOVA). Data represent means ± sd (n > 15) of two independent biological replicates.