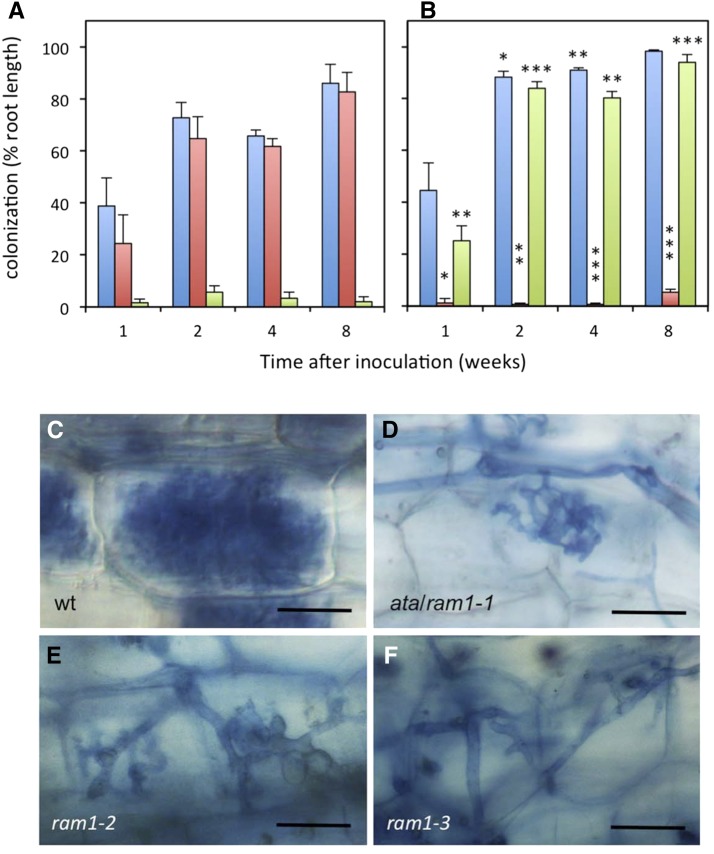
Figure 2.
ata mutants can be colonized from nurse plant inoculum but retain the arbuscule phenotype. A, Root colonization in the wild type (wt; petunia line W138) colonized by R. irregularis from nurse plants. Total root colonization (blue) and occurrence of arbuscules (red) and abnormal arbuscules (green) are indicated. B, Root colonization in the ata mutant colonized by R. irregularis from nurse plants (same color code as in A). Asterisks indicate significant differences between the mutant and the wild type. C to F, Appearance of arbuscules in the wild type (C), ata (D), ram1-2 (E), and ram1-3 (F). Columns represent the average of five biological replicates ± sd. Significant differences (Student’s t test) between the mutant and the wild type are indicated with asterisks (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001). Bars = 25 µm.