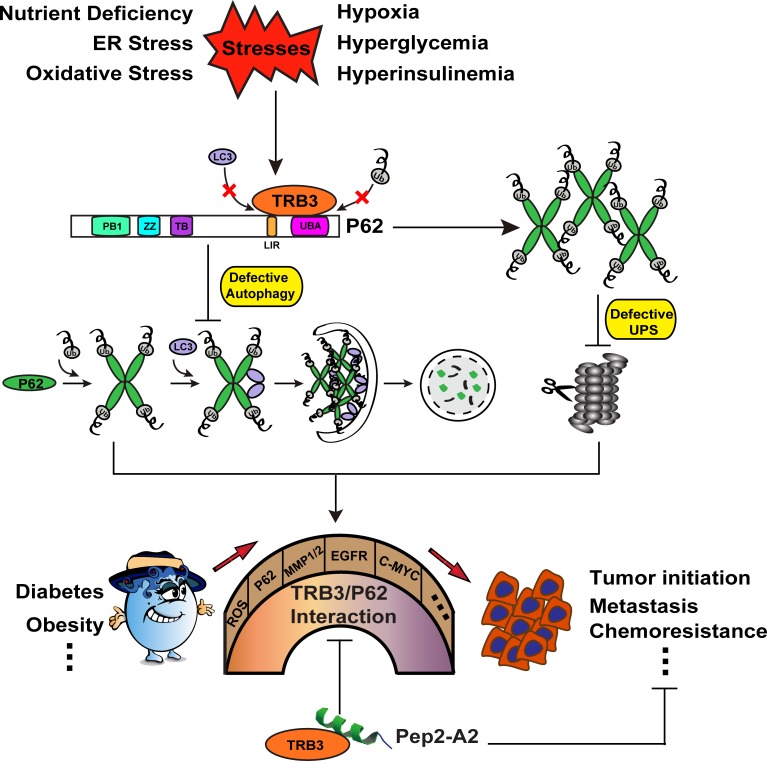
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the TRIB3-P62 interaction in the connection of diabetes to cancer promotion.
Many stresses can increase the expression of TRIB3 and enhance the interaction between TRIB3 and P62. The TRIB3-P62 interaction abrogates the binding of LC3 and ubiquitinated substrates to P62, which induces the blockage of autophagic flux and subsequent UPS defect. UPS and autophagy are considered as the last line of defense in protein quality control. Dysfunction of the two degradation systems results in the accumulation of ROS and a multitude of cancer-promoting factors, which act as bricks or stones to build a bridge for connecting diabetes to tumor promotion. P62-derived α-helical peptide (Pep2-A2) can interfere with the TRIB3-P62 interaction and produce a potent antitumor effect, suggesting that the TRIB3-P62 interaction is a candidate therapeutic target against cancer.