Figure 7. Modulation of intracellular calcium by ionomycin or BAPTA-AM affects surface PS in human cancer cells.
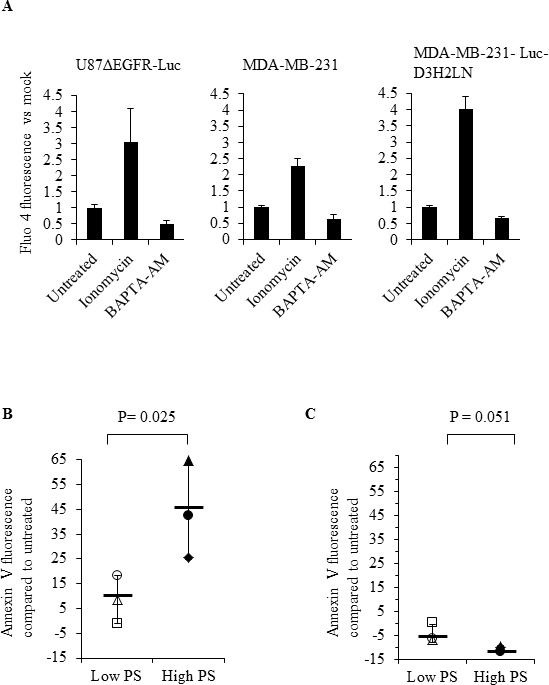
A. Cells were treated with DMSO, ionomycin or BAPTA-AM, incubated with the calcium binding dye Fluo-4 Direct and fluorescence was measured using a microplate reader. Bars show relative changes in Fluo-4 Direct fluorescence signal for each cell line normalized to DMSO controls. B. Low and high surface PS cells were treated with DMSO or ionomycin and surface PS levels were assayed by staining with annexin V FITC, followed by flow cytometry. The axis indicates shift in the geometrical mean of annexin V FITC fluorescence in ionomycin treated vs untreated cells (U87ΔEGFR-Luc □, H1299 Δ, MDA-MB-231 ○, MDA-MB-231-Luc-D3H2LN ◆, Gli36 ▲, U373 ●, Mean—). (C) Low and and high surface PS cells were treated with DMSO or BAPTA-AM, followed by incubation with annexin V FITC and analyzed by flow cytometry. The axis indicates shift in the geometrical mean of annexin V FITC fluorescence in BAPTA-AM treated vs untreated cells (U87ΔEGFR-Luc □, H1299 Δ, MDA-MB-231 ○, MDA-MB-231-Luc-D3H2LN ◆, Gli36 ▲, U373 ●, Mean—).
