Figure 7. Knockdown of EMP3 reduces the expression and activity of PI3K in SK-Hep-1 cells and the proposed roles of EMP3 in HCC proliferation and invasion.
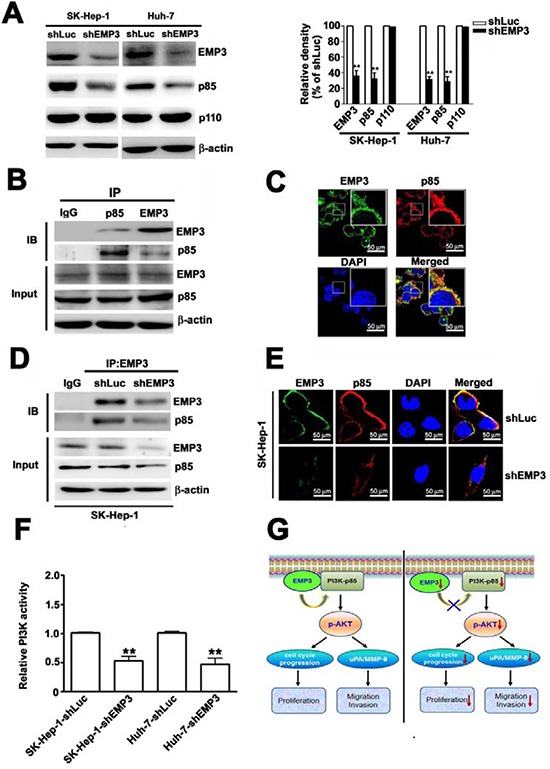
A. The protein amounts of EMP3, p85 regulatory subunit and p110 catalytic subunit of PI3K, and β-actin were determined by immunoblotting. The quantitative amounts of indicated proteins were shown in the right plot. B. The association between EMP3 and p85 in SK-Hep-1 cells was examined by the reciprocal immunoprecipitation (IP) / immunoblotting (IB) with anti-EMP3 and anti-p85 antibodies as indicated in the upper panel. The lower panel showed the input of the indicated protein in cell lysate. C. The localization of EMP3 (green) and p85 (red) in SK-Hep-1 cells were determined by IF staining. The cell nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue). D. The association of EMP3 and p85 in shLuc-SK-Hep-1 cells and in shEMP3-SK-Hep-1 cells were examined by IP/IB against EMP3 and p85, respectively. The lower panel showed the input of the indicated protein in cell lysate. E. The localization of EMP3 (green) and p85 (red) were determined by IF staining and cell nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue) in SK-Hep-1 cells. F. The relative kinase activity of PI3K was shown. G. The role of EMP3 in cell proliferation and invasion of HCC was illustrated. Left plot: EMP3 associates with PI3K-p85 involved in activation of PI3K/Akt pathway to promote cell cycle progression and proliferation, and also to enhance uPA/MMP-9 required for migration and invasion in HCC cells. Right plot: targeting EMP3 with shRNA to decrease the level of EMP3 results in reduction of PI3K-p85 and inactivation of PI3K/Akt, which contribute to inhibition of cell proliferation and suppression of migration and invasion by down-regulation of uPA/MMP-9 cascade in HCC cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01. Scale bars = 50 μm.
