Figure 1. In samples of invasive carcinoma of no special type, MCM2 expression is highest and MCM2 frequently colocalizes with CSC markers in TNBC specimens.
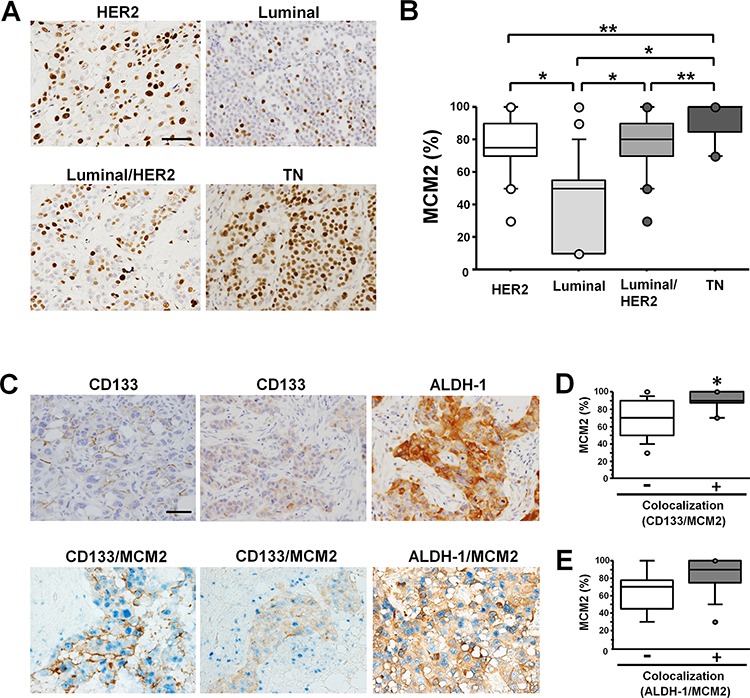
A. MCM2 immunohistochemical staining of invasive carcinomas of no special type showing representative features of the HER2 group (top-left), luminal group (top-right), luminal/HER2 group (bottom-left), and TN group (bottom-right). Scale bar indicates 100 μm. Note the frequent nuclear signals in the TNBC case. B. Labeling index of MCM2 in each breast cancer subtype. The index of the TN type (n = 20) of breast cancer was significantly higher than the indices of the HER2 (n = 30), luminal (n = 25), and luminal/HER2 (n = 29) types. *P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test. C. Immunostaining for CD133 in cases with invasive carcinoma of no special type. CD133 antigen localized to the cell membrane (top-left) or the cytoplasm (top-middle). Immunostaining for ALDH-1 in breast cancer (top-right). Double immunostaining for CD133 (brown) and MCM2 (blue) (bottom-left, middle). Double immunostaining for ALDH-1 (brown) and MCM2 (blue) (bottom-right). Scale bar indicates 100 μm. D. The labeling index of MCM2 in the CD133/MCM2 colocalized group (n = 17) and non-colocalized group (n = 10). *P < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test. E. The labeling index of MCM2 in the ALDH-1/MCM2 colocalized group (n = 15) and non-colocalized group (n = 5).
