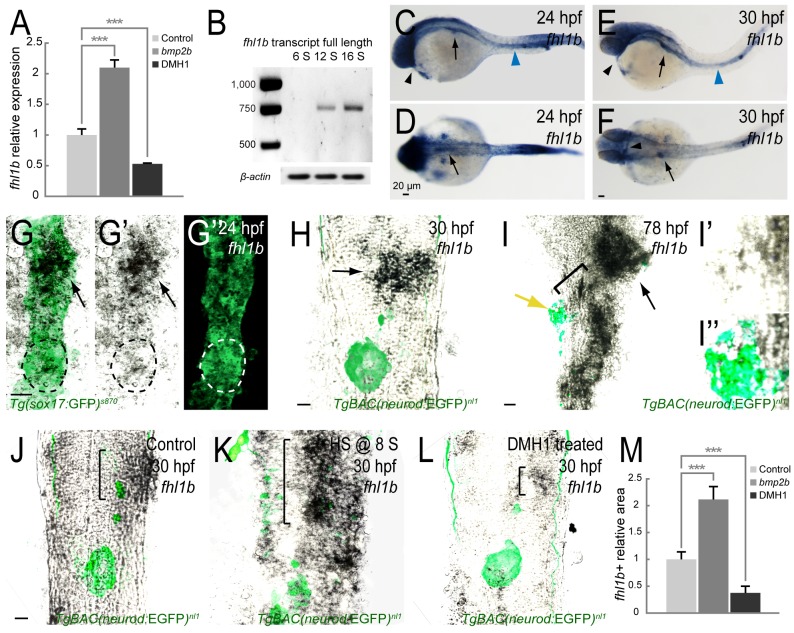
Fig 1. fhl1b is a target of the Bmp2b pathway.
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of fhl1b in bmp2b-overexpressing or DMH1-treated embryos at 20 hours-post-fertilization (hpf). Gene expression was normalized to that of β-actin and presented as fold changes (mean±SD) against control expression. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: ***, P < 0.001. (B) fhl1b full-length transcript, which was detected by RT-qPCR analysis of whole embryos, starts to be expressed from the 12-somite stage onwards. (C-F) Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing the expression of fhl1b at 24 (C-D) and 30 (E-F) hpf. At 24 hpf (C-D), fhl1b is expressed in the anterior part of the endoderm, which corresponds to the prospective liver anlage (black arrows). Additionally, fhl1b is expressed in the pronephric duct (blue arrowhead) and heart (black arrowhead). At 30 hpf (E-F), fhl1b continues to be highly expressed in the liver (black arrows) and remains to be expressed in the pronephric duct (blue arrowhead) and heart (black arrowheads). (G-G”) Double antibody and in situ hybridization staining of fhl1b at 24 hpf in Tg(sox17:GFP)s870 embryos. fhl1b is primarily expressed in the anterior part of the endoderm, which corresponds to the prospective liver anlage (black arrows). White and black dotted circles locate the dorsal pancreatic bud, which gives rise exclusively to the principal islet, a cluster of endocrine cells. A merged view of G’ and G” is shown in G. (H-I”) Double antibody and in situ hybridization staining of fhl1b in TgBAC(neurod:EGFP)nl1 embryos at 30 (H) and 78 (I-I”) hpf. TgBAC(neurod:EGFP)nl1 expression marks the posteriorly located pancreatic endocrine cells. At 30 hpf (H), fhl1b is highly expressed in the liver (black arrow). At 78 hpf (I-I”), the level of fhl1b expression is continuously high in the liver (black arrow) and in patches of cells in the distal intestine, low in the HPD system (black bracket), and absent in most of the pancreatic cells except for a few cells in the periphery of the principal islet (yellow arrow). In the principal islet, fhl1b expression is confined to the peripheral boundary and does not significantly overlap with the TgBAC(neurod:EGFP)nl1 expression. Magnified images of fhl1b and TgBAC(neurod:EGFP)nl1expression in the principal islet are shown in I’ and I”. (J-L) Double antibody and in situ hybridization staining showing the endogenous expression of fhl1b in the liver (black brackets), comparing control (J), bmp2b-overexpressing (K), and DMH1-treated (L) TgBAC(neurod:EGFP)nl1 embryos at 30 hpf. fhl1b expression was greatly expanded when bmp2b expression was induced at the 8-somite stage (K), but was reduced in DMH1-treated embryos (L). (M) Quantification of the fhl1b-positive in situ hybridization signal at 30 hpf. The areas of fhl1b-positive signal were selected and measured using Image J with normalization to control. 3 individual embryos were analyzed for each condition. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: ***, P < 0.001. G-L, confocal single-plane in situ hybridization images combined with the projection images of Tg(sox17:GFP)s870 (G-G”) and TgBAC(neurod:EGFP)nl1 (H-L) expression, ventral views, anterior to the top. C and E, lateral views, anterior to the left. D and F, dorsal views, anterior to the left. n = 10 per each time point and condition. Scale bars, 20 μm.