Figure 1. Effects of normobaric oxygen and melatonin on disseminate neuronal injury.
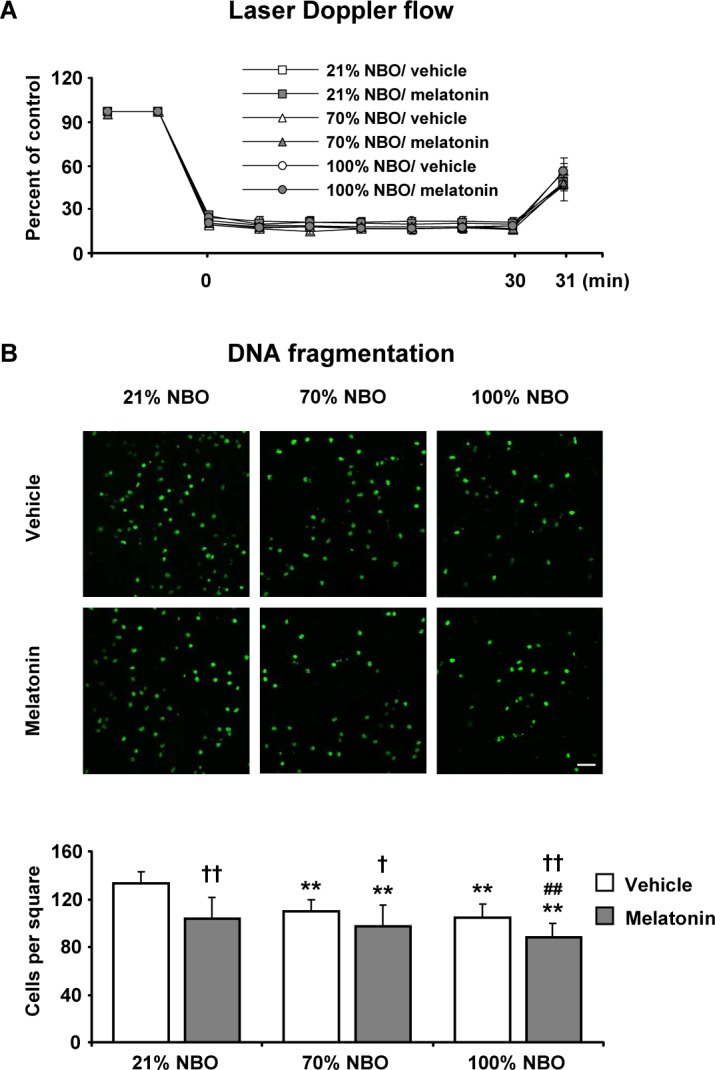
A. Laser Doppler flow (LDF) recordings during ischemia and initial reperfusion and B. disseminate neuronal injury in the striatum assessed by terminal transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) in mice submitted to 30 min of intraluminal middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo), which induces disseminate neuronal injury in the striatum [3, 21]. During the first 90 min of reperfusion, mice had been exposed to 21% (ambient air), 70% and 100% normobaric oxygen (NBO). Vehicle or melatonin (4 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally administered after reperfusion onset, and mice were sacrificed 72 hours later. Note that the number of TUNEL+ (i.e., DNA-fragmented) cells is significantly decreased by NBO alone and melatonin alone and furthermore synergistically reduced by combined NBO and melatonin exposure. Data are mean ± S.D. values (n = 7-8 mice/group). **p < 0.01 compared with corresponding mice exposed to 21% NBO; ##p < 0.01 compared with corresponding mice exposed to 70% NBO; ††p < 0.01/†p < 0.05 compared with corresponding mice receiving vehicle.
