Figure 5. PRMT6-mediated p21 methylation affects p21 phosphorylation and chemosensitivity of cancer cells.
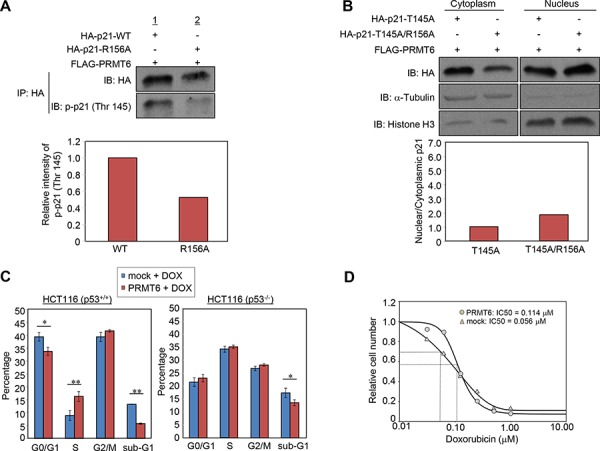
A. Wild-type or arginine 156-substituted p21 and PRMT6 were co-overexpressed in 293T cells and phosphorylation levels of the p21 proteins at threonine 145 were examined following immunoprecipitation. The signal intensity of phosphor-p21 (Thr 145) was quantified and normalized by p21 amount. B. Threonine 145-substituted p21 mutant (p21-T145A) or threonine 145/arginine 156 double substituted p21 mutant (p21-T145A/R156A) and PRMT6 were co-overexpressed in HCT 116 p53+/+ cells. Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were prepared and analyzed by western blot. The signal intensity of p21 bands in each fraction was quantified and normalized by that of α-Tubulin or histone H3. C. HCT 116 p53+/+ (left) or HCT116 p53−/− (right) cells were transfected with mock or PRMT6 expression vector and incubated for 40 h. Subsequently, the cells were further incubated in the presence of 0.5 μM doxorubicin for additional 8 h. Cell cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry coupled with BrdU staining. P-values were calculated with Student's t test (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). D. HCT116 p53+/+ cells transfected with a mock vector or a PRMT6 expression vector were treated with various concentrations of doxorubicin 24 h post transfection. Cell viability was measured 96 h after the drug treatment. IC50 was calculated using the SigmaPlot software.
