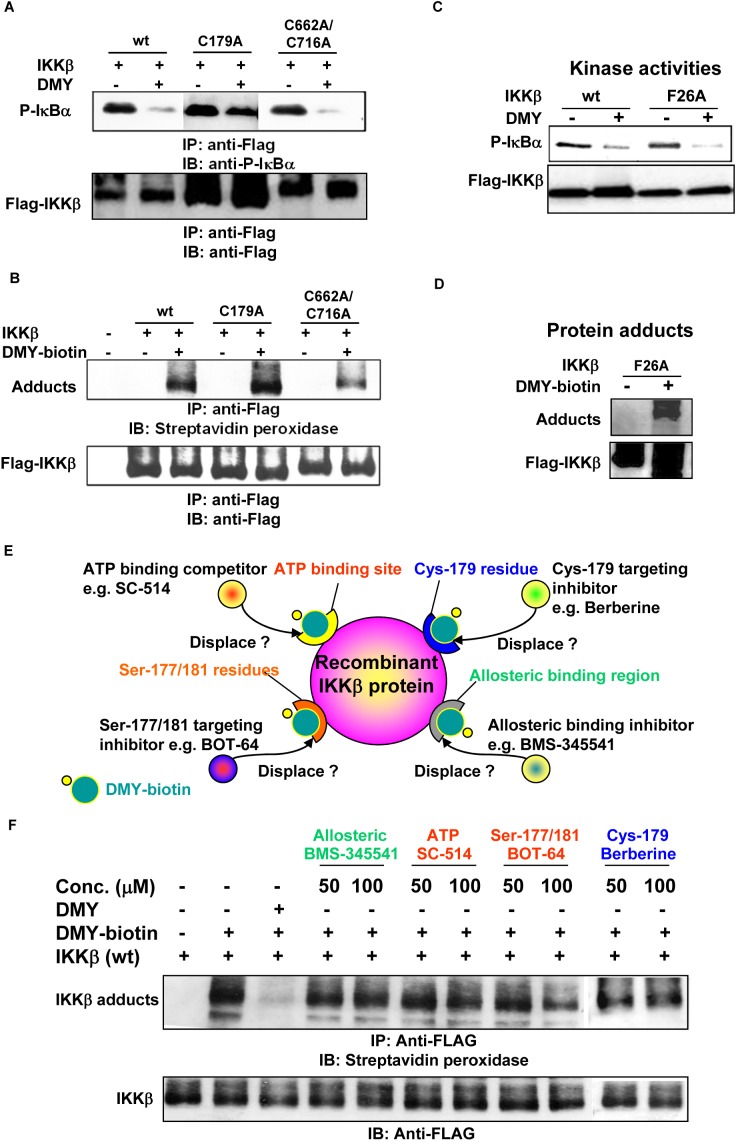
Figure 5. Identification of a novel drug-binding site on IKK-β using the small molecule DMY.
A. DMY inhibited the kinase activity of IKK-β (C179A) and IKK-β (C662A/C716A). B. DMY-biotin formed protein adducts with IKK-β (C179A) and IKK-β (C662A/C716A). C. DMY circumvented the drug-resistant phenotype of IKK-β (F26A) with an ATP-binding site mutation. D. DMY-biotin formed protein adducts with IKK-β (F26A). HEK293 cells transfected with WT or mutant FLAG-IKK-β plasmid were immunoprecipitated for kinase activity assay and protein-adduct formation assay. The protein adducts formed between mutant IKK-β and DMY-biotin were visualized by streptavidin peroxidase. E. Schematic diagram showing the novel site on IKK-β responsible for DMY binding. F. DMY-biotin probe assisted IKK-β displacement binding assay. HEK293 cells transfected with FLAG-IKK-β(WT) plasmid were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody. The IP Flag-IKK-β was incubated with 100 μM DMY-biotin in the presence of the indicated concentrations of DMY, berberine, SC-514, BMS-345541 or BOT-64. The DMY-biotin signal was detected by Western blotting using streptavidin peroxidase.