Figure 2. sMEK1 decreases VEGF-stimulated VEGFR-2 phosphorylation (Tyr-951).
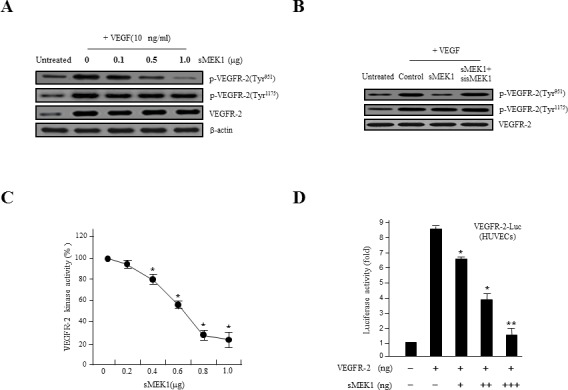
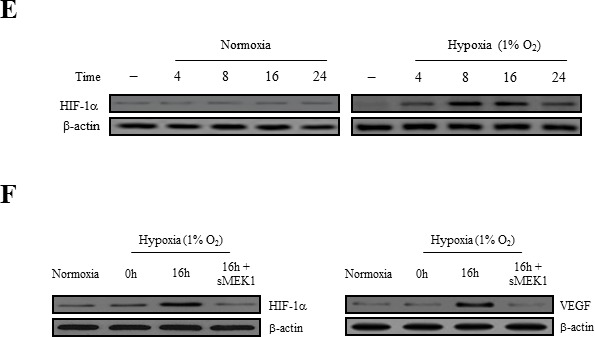
A. HUVECs were transfected with different concentrations of sMEK1, and total cell lysates were prepared. The expression of total and phosphorylated (Tyr-951 or Tyr-1175) VEGFR-2 was measured by immunoblot analysis in cells treated with VEGF. B. HUVECs were treated with VEGF and then transfected with the control vector, sMEK1, or sMEK1 plus sisMEK1. sMEK1 suppressed VEGF-stimulated VEGFR-2 (Tyr-951) phosphorylation. VEGFR-2 (Tyr-951 or Tyr-1175) phosphorylation was evaluated using specific antibodies, and VEGFR-2 was used as a loading control. C. sMEK1 suppressed VEGFR-2 kinase activity in vitro, analyzed using an in vitro HTScan VEGFR-2 kinase assay kit followed by colorimetric detection according to the manufacturer's protocols. Values are presented as means±SDs; *, P < 0.05 vs. control. D. sMEK1 suppresses VEGFR-2-dependent transcription. HUVECs were co-transfected with 500 ng VEGFR-2-Luc, 500 ng VEGFR-2 expression plasmid (pcDNA3.1/VEGFR-2), and increasing concentrations of a plasmid encoding sMEK1 (pcDNA3.1/Flag-sMEK1) (50, 250, and 500 ng). Each data point represents triplicate samples, and the bars indicate means±SDs. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 vs. control. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. E. HUVECs were seeded and then grown under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 4, 8, 16, or 24 h. HIF-1α protein accumulation was measured by immunoblot analysis. F. sMEK1 inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF and HIF-1α activation. HUVECs were transfected with sMEK1 for 16 h under either normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Equal protein amounts were introduced to SDS-PAGE, blotted, and incubated with either specific primary VEGF, HIF-1α, or β-actin antibody. β-actin was used as a loading control.
