Figure 4. XRCC2 knockdown cells exhibit impaired repair of radiation-induced DNA DSBs.
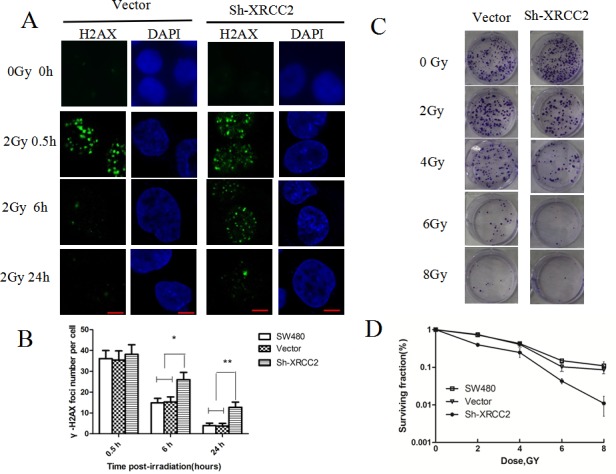
A. The levels of immunofluorescence that were observed in a phosphorylation of H2AX (γ-H2AX) assay. Images of γ-H2AX foci were obtained 0, 0.5, 6, and 24 h after 2 Gy of IR was applied to vector control cells and SW480 cells transduced with shRNA1. B. The average number of γ-H2AX foci per nucleus was calculated based on the number of γ-H2AX foci that were detected in more than 100 cells for each treatment group. The error bars represent the SD from three independent experiments. Statistical differences between the numbers of γ-H2AX foci in the control cells (SW480 and vector alone) and the shXRCC2 cells 6 h and 24 h after an IR treatment were calculated (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). C. Representative images of the clonogenic cell survival assays that were performed. IR treatment inhibited the colony-forming capacity of the cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, sh-XRCC2 enhanced the tumor suppressive effect of the IR. D. The survival fraction curves for the SW480, vector, and sh-XRCC2 cells that were tested in clonogenic survival assays. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
