Figure 2. Both L2-IL-1β and K14-CDX2::L2-IL-1β mice demonstrate equivalent inflammatory activity.
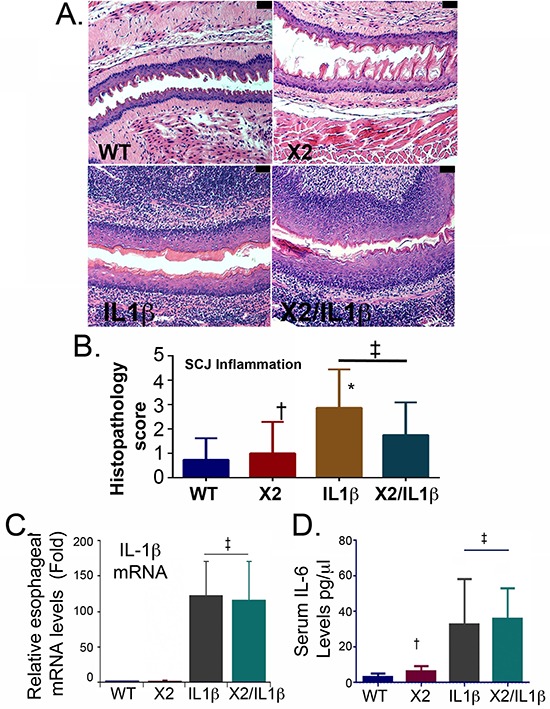
A. Histopathologic alterations in the esophagus of L2-IL-1β and K14-Cdx2::L2-IL-1β transgenic mice (X100 magnification; black bar = 50 μm). WT: wild-type; X2: K14-Cdx2; IL-1β: L2-IL-1β; and X2/IL-1β: K14-Cdx2::L2-IL-1β. B. Score of inflammation at SCJ by observers blinded to genotype at 14 months of age. L2-IL-1β and K14-Cdx2::L2-IL-1β mice develop increased inflammation that is significant different from WT mice but not different from each other. ‡ Not significantly different, (adjusted p = 0.40); † not significantly different from WT control (adjusted p > 0.99); * significantly differs from WT mice (adjusted p ≤ 0.0002) by Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA and Dunn's multiple comparisons testing. C. Determination of esophageal IL-1β mRNA levels by qPCR analysis. Significance determined by one-sided ANOVA and Tukey's Multiple Comparison testing, n = 6 for each line. (‡ both significantly differ from WT control adjusted p < 0.01 but no significant difference between L2-IL-1β and K14-CDX2/L2-IL-1β mice). D. ELISA for serum levels of IL-6, n = 4. († not significantly different from WT mice by one-sided ANOVA and Tukey Multiple comparisons testing, adjusted p = 0.99; ‡ both significantly differ from WT control adjusted p < 0.03 but no significant difference between each other).
