Figure 3. A35 induces top2α-DNA cleavage complex formation by enhancing pre-strand and post-strand cleavage and inhibiting DNA religation.
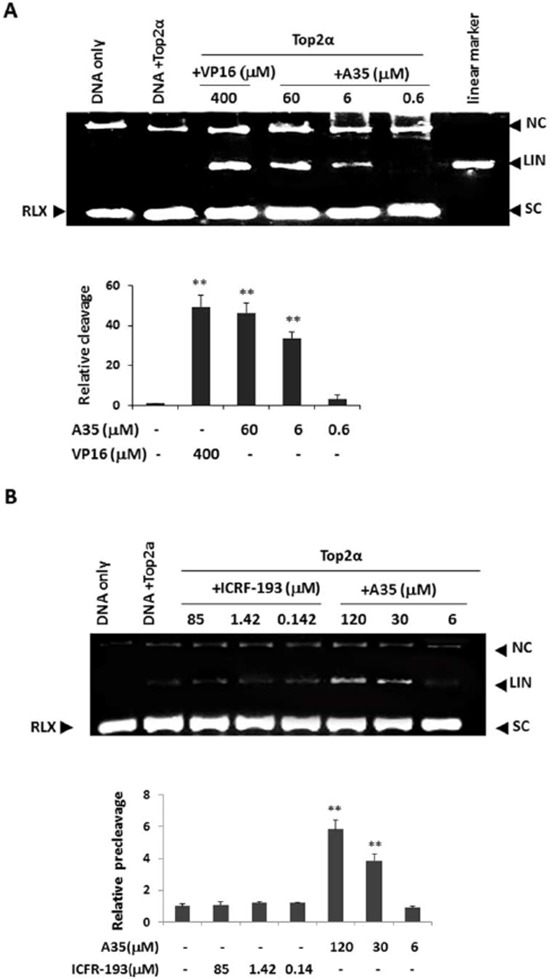
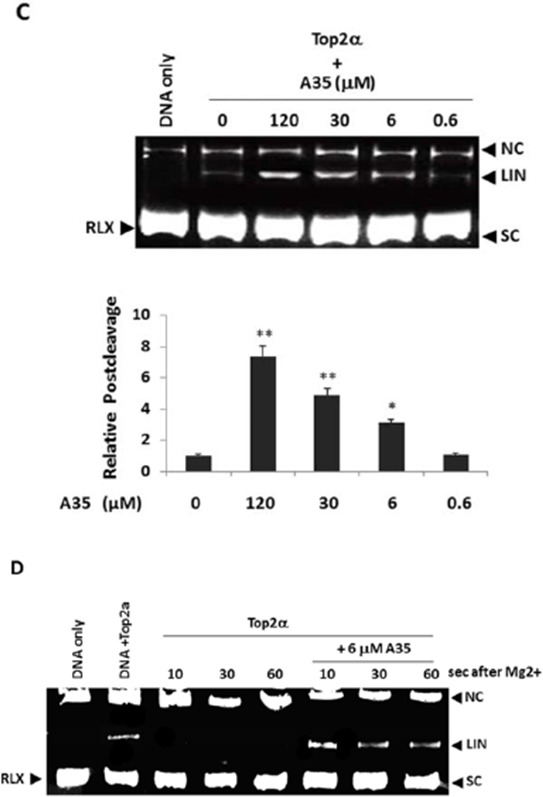
A. The supercoiled plasmid pBR322 was incubated with purified top2α (8U) with or without the indicated concentrations of A35. Reaction products were separated by 1.4% agarose gel electrophoresis in the presence of the nucleic staining agent EB to allow for the separation of supercoiled (SC), relaxed closed-circular (RLX), linear (LIN) and nicked circular (NC) DNA. The intensities of the linear bands observed were quantified and plotted relative to the control (pBR322+Top2α). B. To determine the effects of A35 on top2α-mediated pre-strand passage cleavage, reactions were performed in the absence of ATP, and the intensities of the linear bands were quantified and plotted relative to the control (pBR322DNA+Top2α). C. Top2α-mediated post-strand passage DNA cleavage affected by A35 was carried out in a reaction buffer containing AMPPNP (1 mM) instead of ATP, and the resulting graph was constructed. D. Top2α-mediated religation of the pBR322 plasmid was examined in the presence or absence of A35. Kinetically competent top2-DNA complexes were trapped in the presence of Ca2+ and in the absence of ATP. After the addition of A35, reactions were reinitiated with Mg2+ and trapped at the indicated time points and examined. *P < 0.05;** P < 0.01
