Figure 2. Overexpression of miR-124 or miR-50b inhibits tumor cell progression and increases sensitivity to chemotherapeutics in vitro.
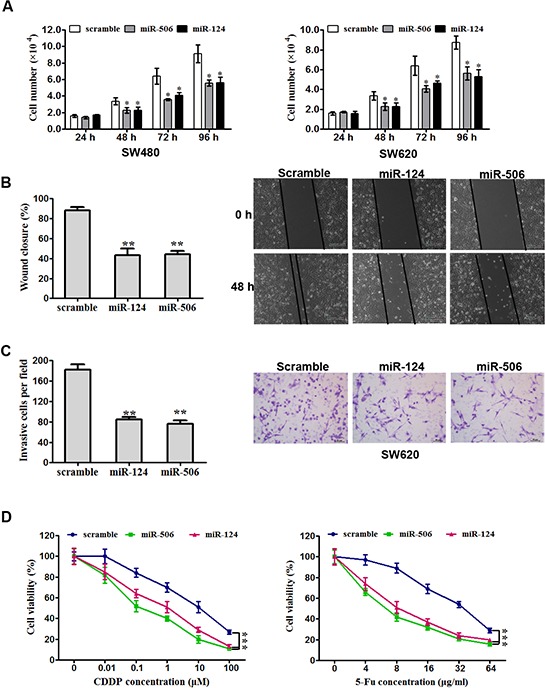
A. SW620 (left) and SW480 (right) cells were transfected with miR-124 mimic, miR-506 mimic or scrambled control. They were then seeded in 12-well plates at a desired cell concentration and maintained in medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. The cells were counted in triplicate at the indicated time points, and their growth rates were recorded. All data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05. B. Scratch wound assays were performed on SW620 cells transfected with miR-124 mimic, miR-506 mimic or scrambled control. The data from three separate assays were averaged and then graphed. All data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m., **P < 0.01. C. An invasion assay was used to quantify cell invasion in a Matrigel-coated chamber. The average number of migrated per field of view from three different experiments is plotted, as described in Materials and methods. Scale bar: 200 mm. All data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m., **P < 0.01. D. An MTT assay was used to evaluate cell viability. Forty-eight hours after transfection with miR-124 mimic, miR-506 mimic or scrambled control, SW620 cells were exposed to a range of CDDP or 5-FU concentrations for 24 h, and the cell viability was determined and recorded. Data are presented as the mean ± SD from at least three separate experiments. ***P < 0.001.
