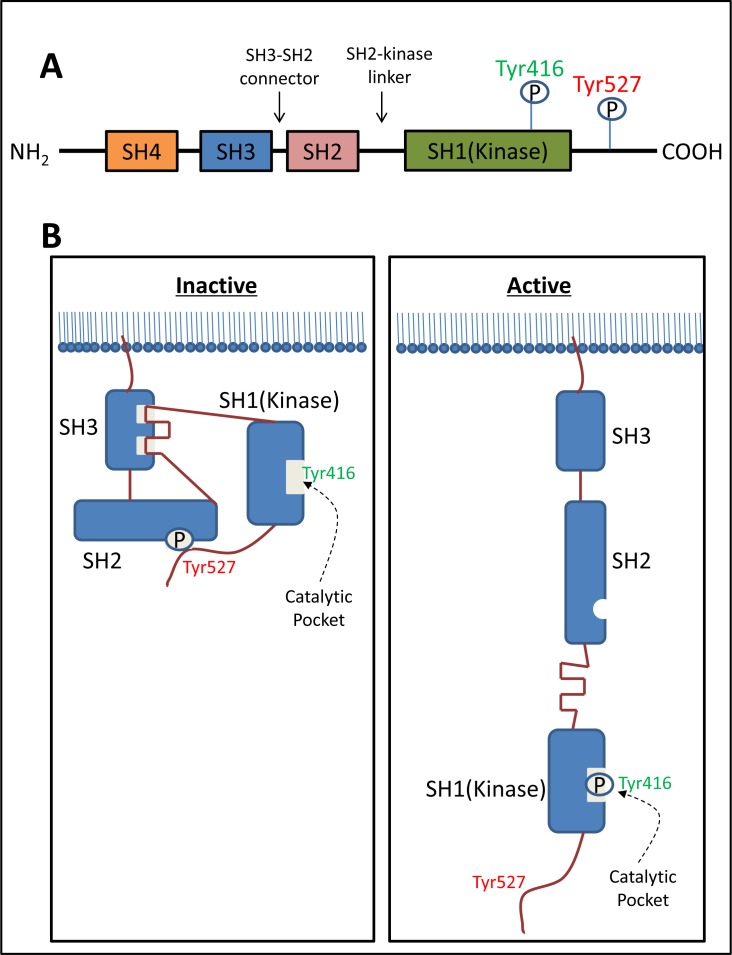
Figure 1. The structure of c-Src and regulation of its kinase activity.
A. Structurally, c-Src consists of a unique Src homology (SH) 4 domain, a SH3 domain, a SH3-SH2 connector, a SH2 domain, a SH2-kinase linker, a SH1-kinase domain, and a C-terminal tail regulatory region. B. The phosphorylation of two tyrosine sites (Tyr416 in the catalytic domain and Tyr527 in C-terminal region) and the intra-molecular interactions among the domains are crucial for the regulation of c-Src activity. Normally c-Src is present in its inactive form, in which Tyr527 is phosphorylated and stabilized by two intra-molecular interactions including: (1) binding of phosphorylated Tyr527 to its own SH2 domain; and (2) binding of the SH2-kinase linker to the SH3 domain. The de-phosphorylation of Tyr527 releases the ‘lock’ from the SH2 domain and causes dramatic conformational change in the kinase domain, subsequently catalyzing the intra-molecular auto-phosphorylation of Tyr416 in the activation loop.