Figure 1. Schematic design and mechanism of functional vincristine plus dasatinib liposomes for the treatment of TNBC and VM channel elimination.
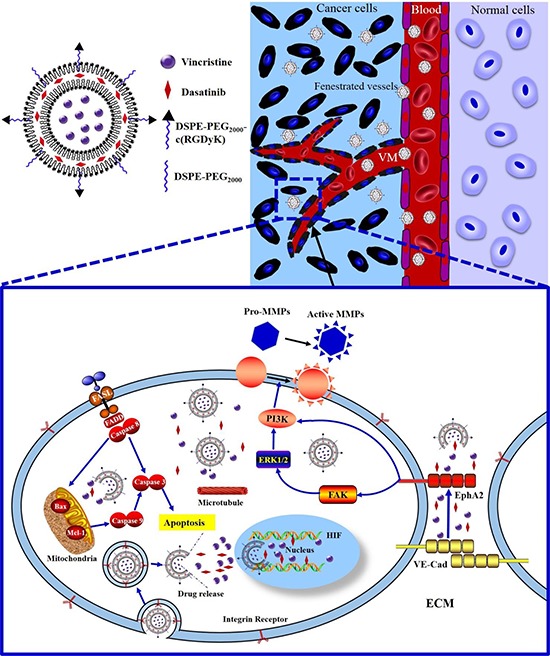
Notes: During hypoxic conditions, the transcription of VE-Cad is increased, and EphA2 is subsequently re-localized to the cell membrane and phosphorylated. Phosphorylated EphA2 directly activates PI3K or initiates the activation of FAK and downstream PI3K. Activated PI3K, in turn, activates MMPs (MMP-2 and MMP-9), which eventually results in VM channel formation. Functional vincristine plus dasatinib liposomes specifically bind to integrin receptors on cancer cells. The internalized liposomes induce the apoptosis of cancer cells through a cascade of apoptotic reactions via the activation of caspase 8, 9, and 3, the increased expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax, the decreased expression of anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1, and generation of ROS. Furthermore, they destroy VM channels via the decreased expression of VE-Cad, FAK, PI3K, MMP-2 and MMP-9.
