Figure 4. The SMO inhibitor Vismodegib partially attenuates UVB-induced BCC development in Ptch1+/−/SKH-1 mice.
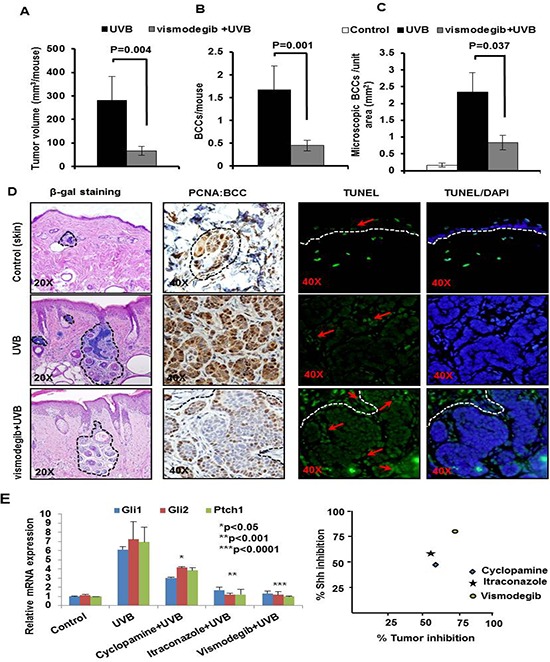
Ptch1+/−/SKH-1 mice were treated with orally administered vismodegib (40 mg/kg body weight twice weekly), 30 min prior to UVB irradiation (180 mJ/cm2). Tumor data were recorded each week. Data showing A. tumor volume/mouse (mm3). B. BCCs/mouse. C. microscopic BCCs/unit area of skin (mm2) of vismodegib- and vehicle-treated in UVB-irradiated Ptch1+/−/SKH-1 mice. D. β-gal staining of UVB-induced microscopic BCCs (magnification 20x), proliferative biomarker (PCNA) (magnification 40x) and TUNEL staining (magnification 40x) in BCCs from vismodegib- and vehicle-treated mice and E. relative ability of vismodegib, ITRA and cyclopamine to inhibit UVB-induced Shh signaling in Ptch1+/−/SKH-1 mice and its correlation with BCC growth inhibition.
