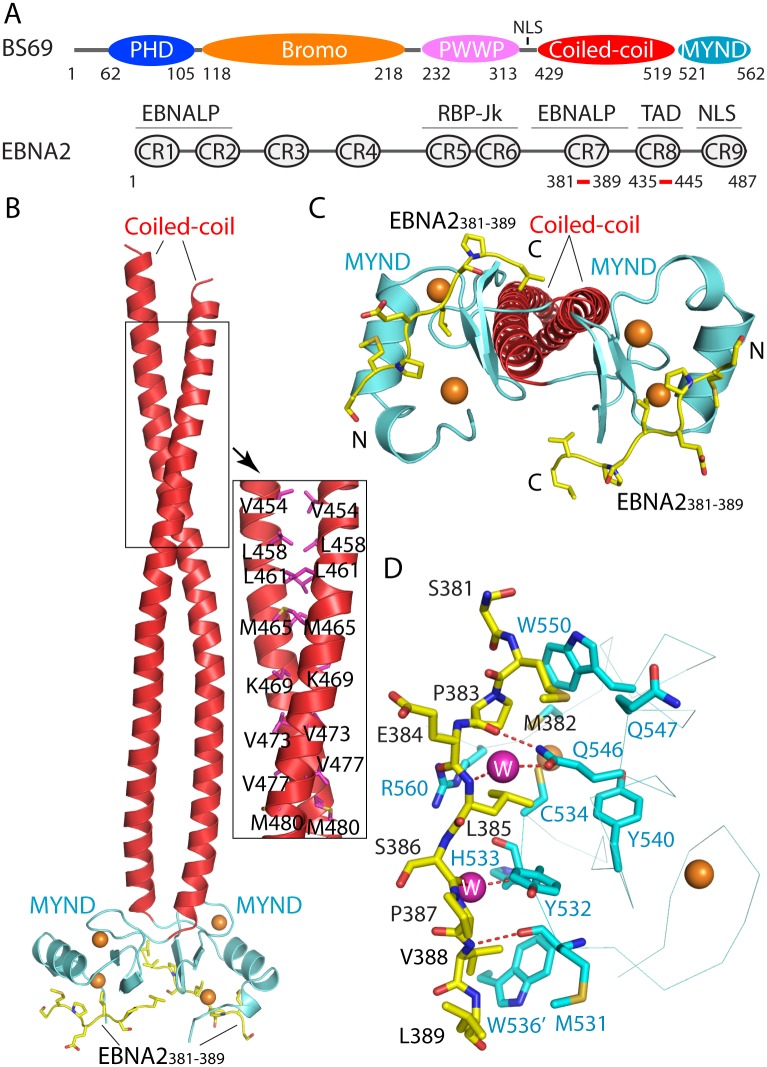
Fig 1. Structural analysis of the BS69CC-MYND domains in complex with the EBNA2381–389 peptide.
(A) Domain architecture of BS69 and EBNA2. Regions responsible for EBNA-LP activation or RBP-Jk binding, transactivation domain (TAD) and nuclear localization sequence (NLS) of EBNA2 are labeled. Note that CR5 contributes to RBP-Jk binding only indirectly [16]. (B) Ribbon representation of the BS69CC-MYND domains (coiled-coil: red; MYND: light blue) in complex with the EBNA2381–389 peptide (yellow sticks). The zinc ions are shown in orange spheres. Selected intermolecular interactions from the coiled-coil domain are shown in the expanded view. (C) Structure of the BS69CC-MYND-EBNA2381–389 complex in a view different from (B). (D) Close-up view of the BS69CC-MYND-EBNA2381–389 interactions. The hydrogen bonds are shown in dashed line. The water molecules are shown in magenta spheres. Residue W536 from the neighboring MYND domain is labeled with an apostrophe mark.