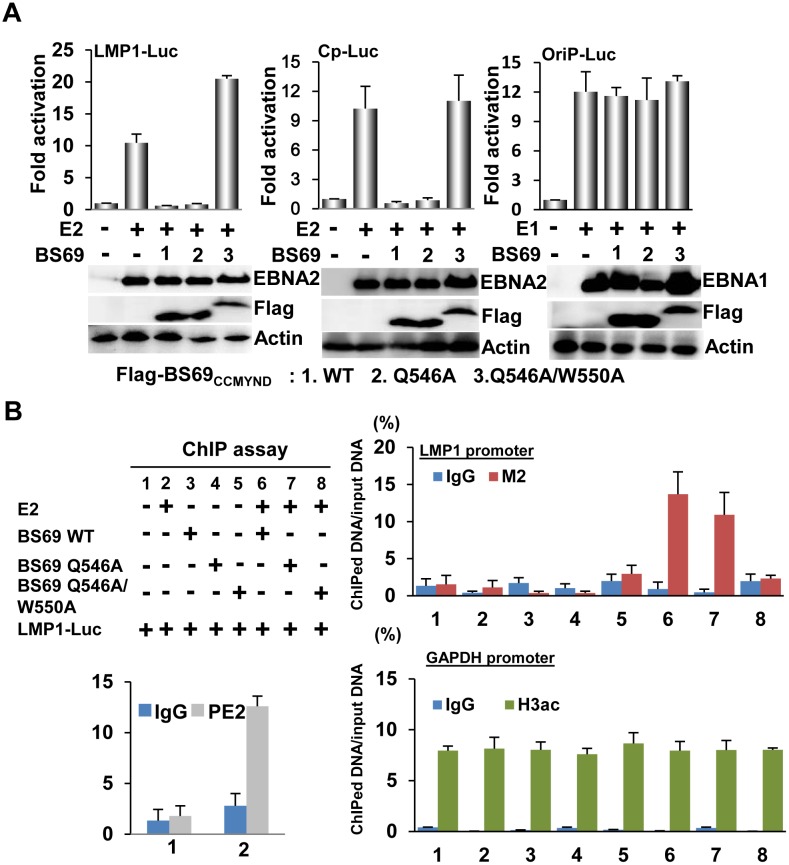
Fig 5. Recruitment of BS69CC-MYND to EBNA2 target promoter through protein interactions leads to down regulation of EBNA2 dependent transcription.
(A) EBNA2 specific reporter plasmids, LMP1-Luc and Cp-Luc, EBNA1 specific oriP-Luc reporter plasmid, CMV-βGal internal control, and the indicated expression plasmids were subjected to a procedure of transfection-mediated transcription reporter assay. The effects of flag-BS69CC-MYND wild type, Q546A or Q546A/W550A on EBNA2-mediated transcription were determined by the resulting luciferase activity corrected for β-gal activity. (B) The experimental design of the transfection-mediated ChIP assay was shown. M2-conjugated sepharose was used to precipitate flag-BS69CC-MYND wild type, Q546A, or Q546A/W550A while H3ac was used to precipitated acetylated-H3. PE2 (EBNA2) ChIP was used to assay EBNA2 enrichment at transfected LMP1 DNA. IgG was used as negative control. The amount of ChIPed DNA was quantified by real time PCR. The enrichment of BS69CC-MYND wild type, Q546A, or Q546A/W550A at the LMP1 promoter and the enrichment of H3ac at GAPAH promoter were represented as % of input DNA, respectively.