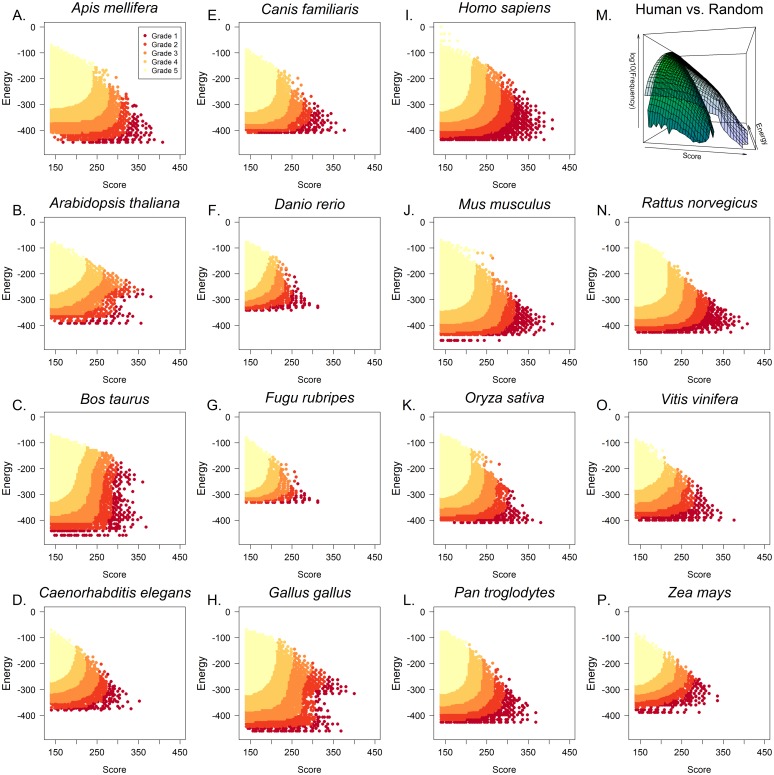
Fig 1. Triplex target sites are enriched in mammalian and non-mammalian genomes.
(A-P) Genome-wide analyses of potential microRNA binding sites in genomic DNA were performed across fifteen species. The heuristic score (”Score”, x-axis) represents Hoogsteen or Reverse Hoogsteen base pair complementarity and Thermodynamic Energy (”Energy”, y-axis) represents the binding energy of the triplex (see Methods). Binding sites were categorized based on the number of hits with better score and energy. Grade 1 hits represent the 99.999th percentile of triplex forming interactions, which are sequences most likely to participate in DNA-microRNA triplex formation. Subsequent grades are 10 fold lower in their percentile ranking (e.g. 99.99, 99.9, 99th percentiles). Additionally, randomly generated DNA sequences were analyzed against human microRNAs. The random DNA sequences (M, green surface) showed many orders of magnitude fewer binding sites than the human genome (M, blue surface) and the identified binding sites were of low quality (low score, high energy).