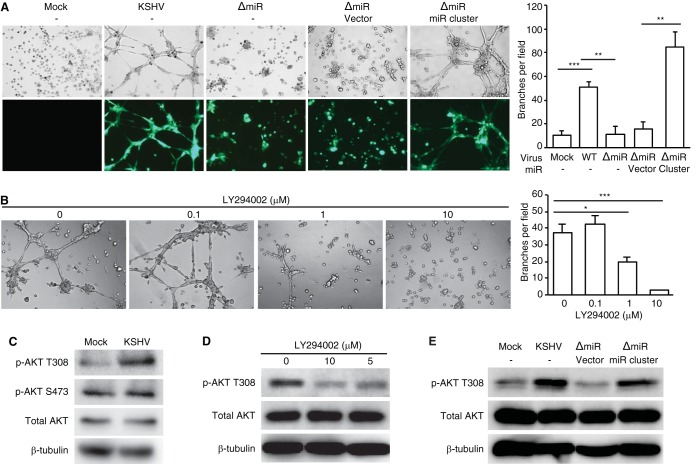
FIG 7 .
KSHV miRNAs mediate KSHV-induced angiogenesis by activating the AKT pathway. (A) The miRNA cluster was required for KSHV-induced angiogenesis. Capillary tube formation activity of uninfected MSCa (Mock), LTC-KMSCa, LTC-ΔmiRMSCa, and LTC-ΔmiRMSCa complemented with vector control or the miRNA cluster. Equal numbers of cells were seeded on top of the Matrigel. Images of tube formation were captured at 8 h postseeding (left panel). Magnification, ×100. The average number of branches per field of view ± SD at ×40 magnification was quantified (right panel). WT, wild type. (B) LY294002 inhibited capillary tube formation of LTC-KMSCa. LTC-KMSCa were incubated with different concentrations of LY294002, and tube formation was analyzed at 8 h postseeding. Representative images (left panel) and the average number of branches per field of view ± SD (right panel) are shown. (C) AKT phosphorylation at T308 but not S473 was enhanced in LTC-KMSCa (KSHV) compared to uninfected MSCa (Mock). (D) LY294002 suppressed AKT phosphorylation at T308 in LTC-KMSCa in a dose-dependent manner. (E) The miRNA cluster was required for AKT phosphorylation at T308. AKT phosphorylation was examined by Western blotting in uninfected MSCa (Mock), LTC-KMSCa (KSHV), or LTC-ΔmiRMSCa (ΔmiR) complemented with vector control (vector) or the miRNA cluster (miR cluster). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.