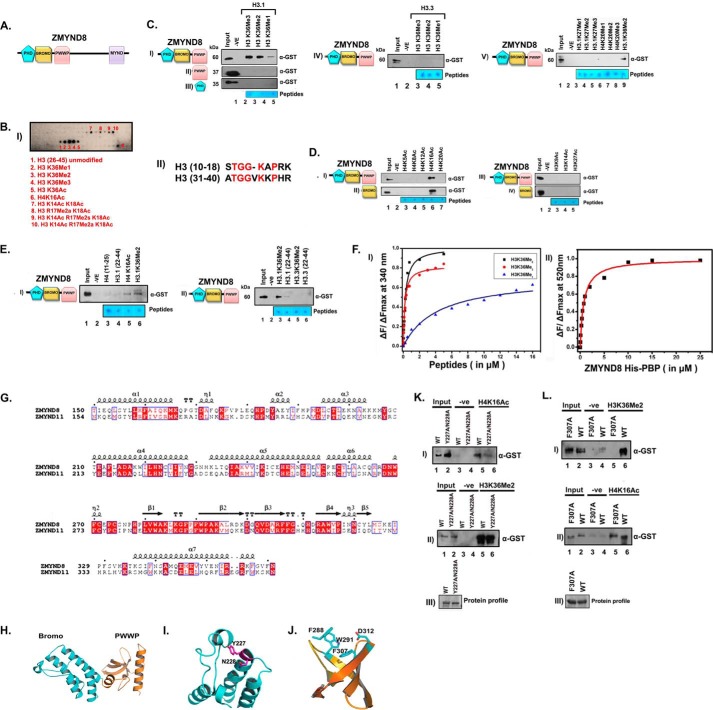
FIGURE 2.
ZMYND8 interacts preferentially with histone H3.1K36Me2/Me3 and H4K16Ac through its putative chromatin-binding module in vitro. A, schematic domain organization of ZMYND8. B, interaction of GST-PBP module of ZMYND8 with MODified Histone Peptide Array (CelluSpots array). Preferential histone peptide interactors of GST-PBP were scored by probing the array with α-GST antibody. GST-PBP showed significant interaction with H3K36Me2 (spot 3), H3K36Me3 (spot 4), and H4K16Ac (spot 6). H3K14Ac K18Ac alone or in combination with R17Me2a/s or H3K18Ac R17Me2a also showed positive interaction (spots 7–10) (panel I). Sequence alignment of the canonical H3(10–18), H3(31–40) by ClustalW. The conserved amino acids are marked in red (panel II). C, interaction of GST-PBP (panel I), GST-PWWP (panel II), and GST-PHD (panel III) with biotinylated mono/di/tri-methylated H3.1K36. Similar interactions of GST-PBP were with H3.3K36-methylated peptides (panel IV). GST-PBP interaction were with biotinylated mono/di/tri-methylated H3K27 and H4K20 peptides (panel V). D, interaction of GST-PBP (panel I), GST-bromo (panel II), with biotinylated H4-K5/K8/K12/K16/K20 acetylated peptides. Interaction of GST-PBP (panel III) and GST-bromo (panel IV) module with other acetylated histone H3 peptides (H3K9Ac, H3K14Ac, and H3K27Ac). E, unmodified H4(11–25) and H3(22–44) (panel I, lanes 3 and 4) showed minimal interaction as compared with H4K16Ac and H3.1K36Me2 peptides (panel I, lanes 5 and 6) with GST-PBP. Furthermore, GST-PBP showed preferential interaction with H3.1K36Me2 compared with H3.3K36Me2 (panel II, compare lanes 3 and 5). F, binding isotherms for the interaction of His-PBP (of ZMYND8) with indicated histone peptides as obtained from steady state fluorescence spectroscopy. Data points for H3K36Me3, H3K36Me2, and H3K36Me1 are indicated by circle (red), square (black), and triangle (blue), respectively (panel I). Binding isotherm for the interaction of His-PBP and H4K16Ac (FAM-conjugated) peptide as obtained from steady state fluorescence spectroscopy (panel II). G, sequence alignment of ZMYND8 and ZMYND11 showing conserved critical residues in Bromo-PWWP (BP) module by using ESPript. H, molecular modeling of ZMYND8 with ZMYND11 BP module was done by using Modeler version 9.13. Modeled bromodomain (I) and PWWP domain (J) structure highlighting the predicted critical residues involved in interaction with acetylated H4K16 and methylated H3.1K36, respectively. K and L, comparative binding ability of GST-PBP wild type (WT) or Y227A/N228A mutant (K) or F307A mutant (L) with H4K16Ac and H3.1K36Me2 peptides (panels I and II).