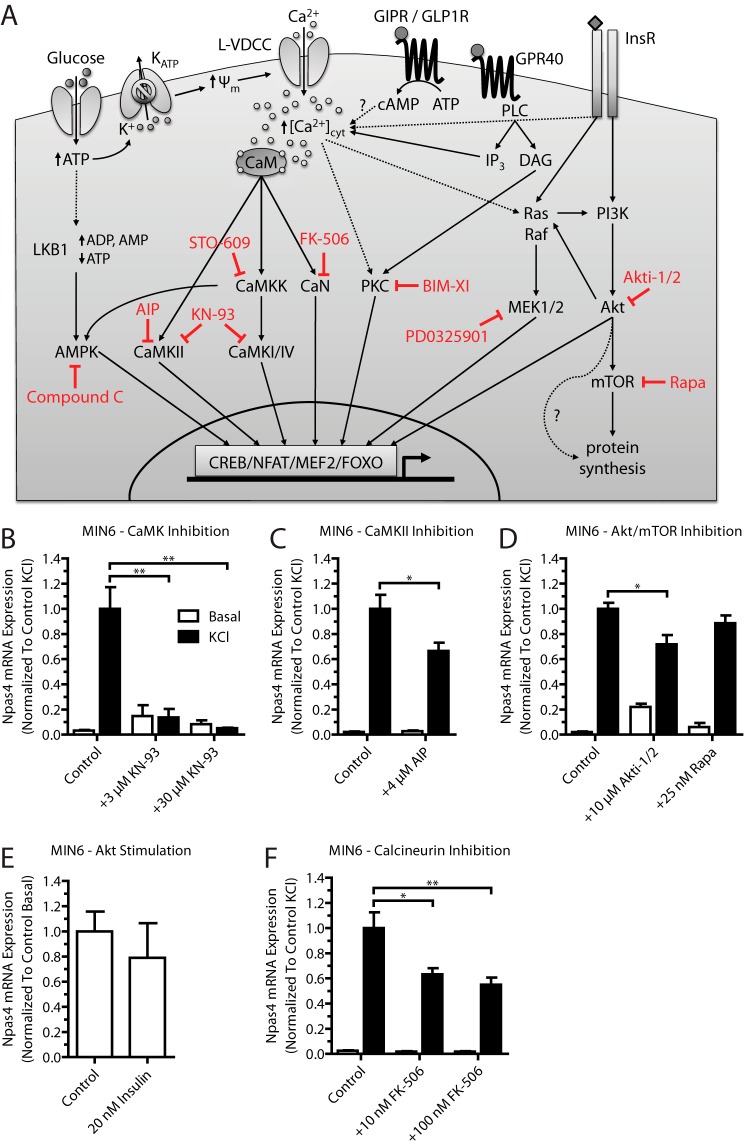
FIGURE 2.
Npas4 mRNA expression in MIN6 beta cells relies on the CaMK, Akt, and CaN signaling pathways. Pharmacological inhibitors for several calcium-dependent signaling pathways were tested for their effect on Npas4 induction. MIN6 cells were kept in either basal medium alone (white columns, Basal) or with 40 mm KCl (black columns, KCl) for 2 h in the presence of inhibitors or vehicle control. RNA was extracted and reverse-transcribed, and TaqMan PCR was carried out for Npas4 using GusB as a reference gene and normalizing to control KCl stimulation. A, simplified schematic of calcium-dependent signaling pathways targeted by pharmacological inhibitors (red). Glucose-induced depolarization and ligand-receptor interaction lead to a rise in cytosolic calcium levels ([Ca2+]cyt) via calcium influx through the L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (L-VDCC) and ER calcium release. The rise in cytosolic calcium levels leads to activation of kinase or phosphatase activity, which, in turn, results in the recruitment of transcription factors to regulatory elements and changes in gene transcription. GIPR, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor; CaM, calmodulin; ψm, mitochondrial membrane potential; InsR, insulin receptor; PLC, phospholipase C; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; BIM-XI, bisindolylmaleimide XI hydrochloride. B, Npas4 induction was prevented completely with the CaMK inhibitor KN-93 at either 3 or 30 μm (n = 3). C, using 4 μm AIP partially reduced Npas4 induction (n = 7). D, Npas4 is regulated by the Akt pathway because treatment with 10 μm Akti-1/2 partially reduces Npas4 mRNA induction, but treatment with 25 nm Rapa had no effect (n = 3). E, treatment with 20 nm human insulin in low-glucose KRBH did not induce Npas4 expression (n = 3). F, the CaN inhibitor FK-506 (tacrolimus) significantly reduced Npas4 induction at doses of 10 and 100 nm (n = 5). Error bars represent mean ± S.E., and significance was determined using a two-tailed Student's t test or a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post hoc analysis and Bartlett's test for equal variances where applicable. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01.