FIGURE 5.
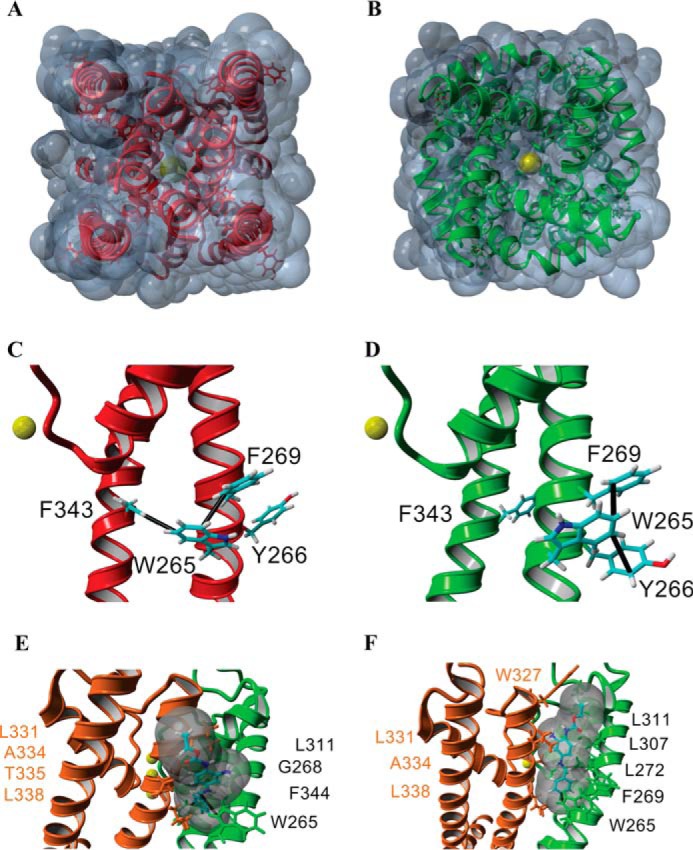
Structural model for the gating transition of the pore in Kv7.3 and the site of action of RTG. A–F, homology models of the Kv7.3 PM in the closed (red, A and C) and open conformations (green, B and D; orange/green, E and F) built using the closed channel structure of KvLm (PDB code 4H33) (22) and open channel structure of Kv1.2-Kv2.1 (PDB code 2R9R) (37). The end view of a solvent-accessible surface map of the closed model (A) shows that the channel is occluded, whereas a similar depiction of the open channel model (B) delineates the presence of K+ in the permeation pathway, consistent with the passage of K+ (yellow, B) through the channel pore. Side views of a single subunit in the closed conformation (C) and in the open conformation (D) highlight predicted π-π interactions (black lines) in each monomer that delineate a change in the interaction partners when the channel gates open. E and F, two low-energy docking models of RTG onto the open channel module (side views), both involving a π-π interaction between Trp-265 and RTG, with amino acids forming the pocket (distance between protein and RTG, <5 Å) labeled explicitly.
