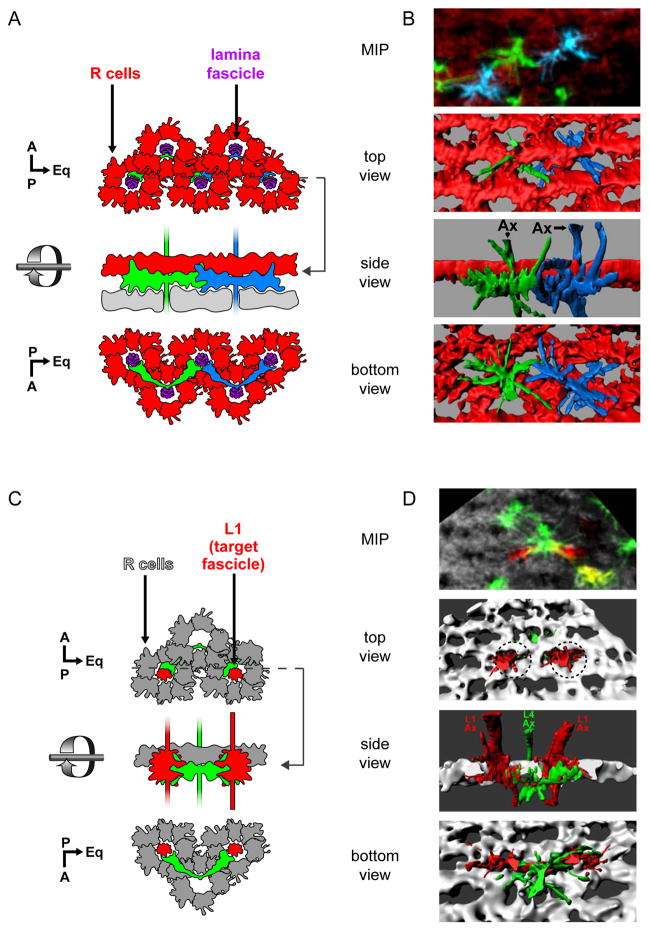
Figure 2. L4 dendrites project to their target fascicles at an early stage in their development.
(A,B) Dendrites from neighboring L4 neurons contact each other as they converge on a common target fascicle at 24 h APF.
(A) Schematic representation of two adjacent L4 neurons (green and blue) imaged in (B). A lattice of R cell growth cones (red) surrounds each lamina fascicle (purple). Glia (grey) lie immediately beneath L4 dendrites. Dotted line indicates the cross-section at which the side view is taken.
(B) Multicolor Flip Out (MCFO; Nern et al., 2015) was used to simultaneously label two adjacent L4s. Confocal sections (top panel; MIP: maximum intensity projection) were used to generate 3D renderings of L4 neurons and R cell growth cones displayed from different perspectives (bottom 3 panels).
(C,D) L4 dendrites make contact with neurons in their target fascicles at 24 h APF.
(C) Schematic representation of (D).
(D) MCFO was used to label an L4 neuron projecting dendrites that contact two L1 neurons, each within its target fascicles (dotted circles). Confocal sections (top panel) were used to create 3D renderings (bottom 3 panels).
Immunofluorescent signals from the MCFO epitopes were false colored in green and blue for L4s in panels B and D. L1 neurons in D are shown in red. R cell growth cones highlighted by anti-Chaoptin (Chp; red in B and grey in D). Other labeled cells are indicated (*), but were not reconstructed. Axons, Ax. Scale bar, 5 μm.