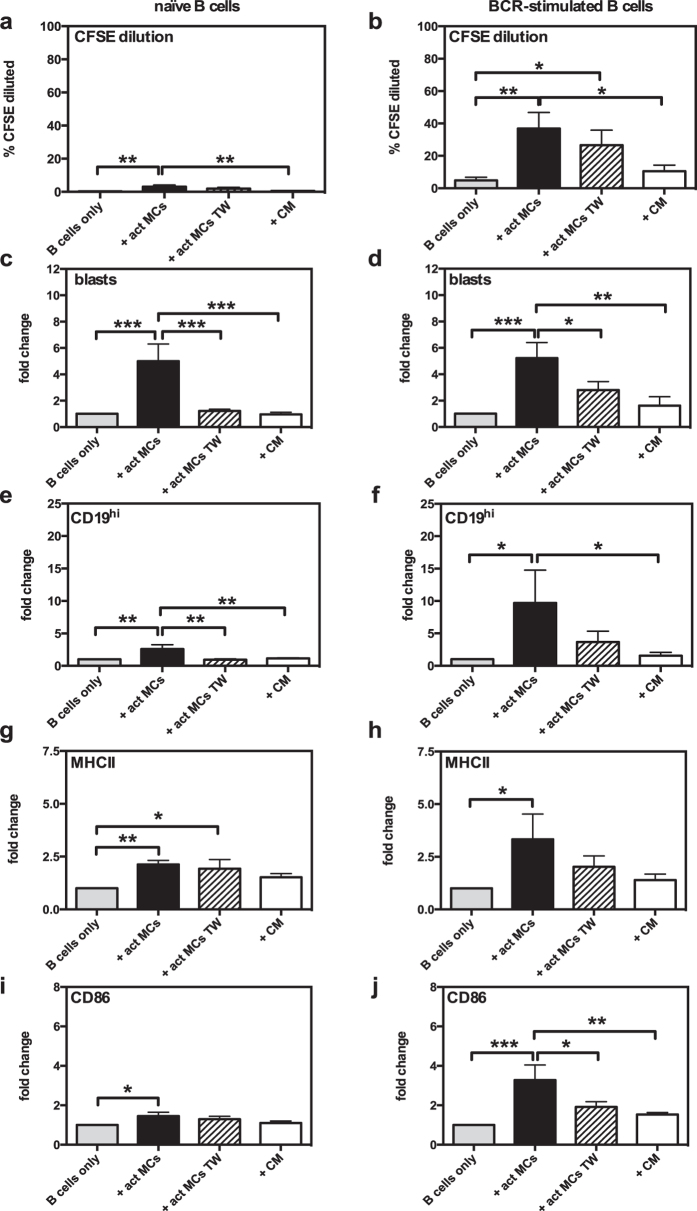
Figure 3. MC-dependent B-cell activation is partially dependent on cell-cell contact.
Antigen-activated MCs (act MCs) were cocultured for 3 days with naïve (a,c,e,g,i) or BCR-activated (b,d,f,h,j) CFSE-labelled splenic B cells, separated or not by a transwell (TW) membrane system. Additional cultures were set up with naïve or BCR-activated CFSE-labelled splenic B cells cultured with conditioned medium (CM) from 3-days old cultures of antigen-activated MCs. Cultures were analysed using flow cytometry and proliferation was assessed as % of B cells with lower CFSE staining intensity than naïve B cells cultured alone (% CFSE diluted; (a,b). Blast formation was determined as % B cells large in forward scatter (c,d), the upregulation of CD19 was expressed as % of total B cells that are CD19hi (e,f), and B-cell expression of MHCII (g,h) and CD86 (i,j) as median fluorescence intensity. Results are expressed as mean % CFSE diluted (a,b) or mean fold-change (as compared to naïve or BCR-activated B cells cultured alone) (c–j) + SEM and represent 3 independent experiments (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. BCR, B-cell receptor; MC, mast cell; MHCII, class II MHC.