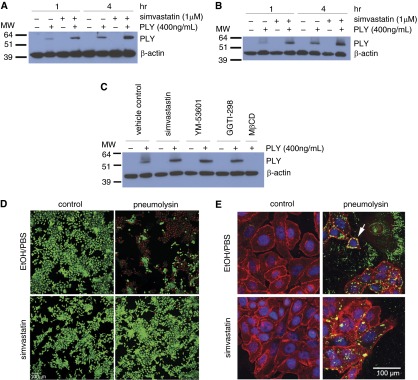
Figure 3.
The presence of pneumolysin in the cell lysate is not reduced by simvastatin. (A and B) HBE1 cells (A) and NHBE cells (B) were treated with 400 ng/ml PLY or mock control with or without 24-hour simvastatin pretreatment. Whole cell lysates were collected 1 or 4 hours after toxin treatment, and immunoblotting was conducted with antibodies against PLY or β-actin. The molecular weight markers are as indicated. Images shown are representatives of three different experiments. (C) NHBE cells were treated with 400 ng/ml pneumolysin or mock control with or without 24-hour simvastatin, YM-53601, or GGTI-298 pretreatment. The 2-mM MβCD pretreatment was done for 30 minutes before the PLY exposure. Whole cell lysates were collected 4 hours after toxin treatment, and immunoblotting was conducted with antibodies against pneumolysin or β-actin. The molecular weight markers are as indicated. The image shown is representative of three different experiments. (D) HBE1 cells were pretreated with 1 μM simvastatin for 24 hours. After the medium change, cells were incubated with 400 ng/ml of PLY or mock control for 4 hours. Cells were stained with Live/Dead assay to assess the membrane damage. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) The cellular localization of PLY. HBE1 cells were pretreated with 1 μM simvastatin for 24 hours. After the medium change, cells were incubated with 400 ng/ml of PLY or mock control for 4 hours. Cells were then fixed and stained with PLY antibody (green), plasma membrane (red), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for nucleus (blue). The white arrow points to the representative PLY binding on the cell membrane. MβCD, methyl-β-cyclodextrin; MW, molecular weight.