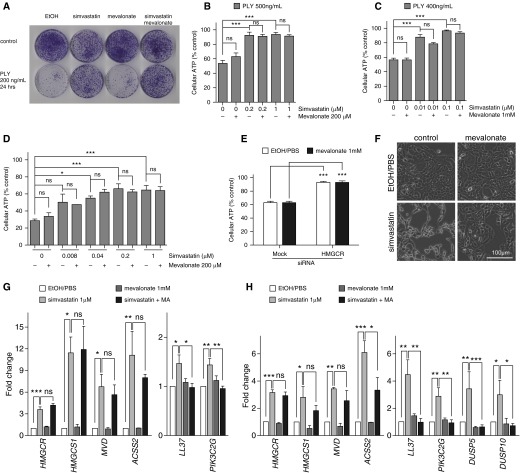
Figure 4.
Simvastatin-mediated protection against pneumolysin is mevalonate independent. (A) HBE1 cells were treated with 1 μM simvastatin with or without 200 μM mevalonate for 24 hours and then removed following 200 ng/ml PLY for 24 hours. Cells were cultured for 10 days to determine the CFUs. (B and C) HBE1 cells were pretreated with the indicted concentrations of simvastatin with or without 200 μM or 1 mM mevalonate for 24 hours and then challenged with PLY for 4 hours. Cell viability was determined by ATP release assay. (D) NHBE cells were pretreated with 1 μM simvastatin with or without 200 μM mevalonate for 24 hours and then challenged with 500 ng/ml of PLY for 4 hours. Cell viability was determined by ATP release assay. (E) The gene knockdown of HMGCR in HBE1 cells mimicked the simvastatin-mediated protection against PLY. The supplement of 1 mM mevalonate did not restore the sensitivity of HMGCR–knocked down HBE1 cells to PLY cytotoxicity. (F) HBE1 cells were treated with 20 μM simvastatin with or without 1 mM mevalonate for 48 hours. (G and H) HBE1 cells (G) and NHBE cells (H) were treated with 1 μM simvastatin with or without 1 mM mevalonate for 24 hours. Total RNA was extracted, and quantitative RT-PCR was conducted to quantify the indicated gene expressions. Asterisks indicate significant statistical difference versus matching control or groups based on one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s (B–D, G and H) or Dunnet’s (E) post test. Error bars represent SEM of at least three experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.