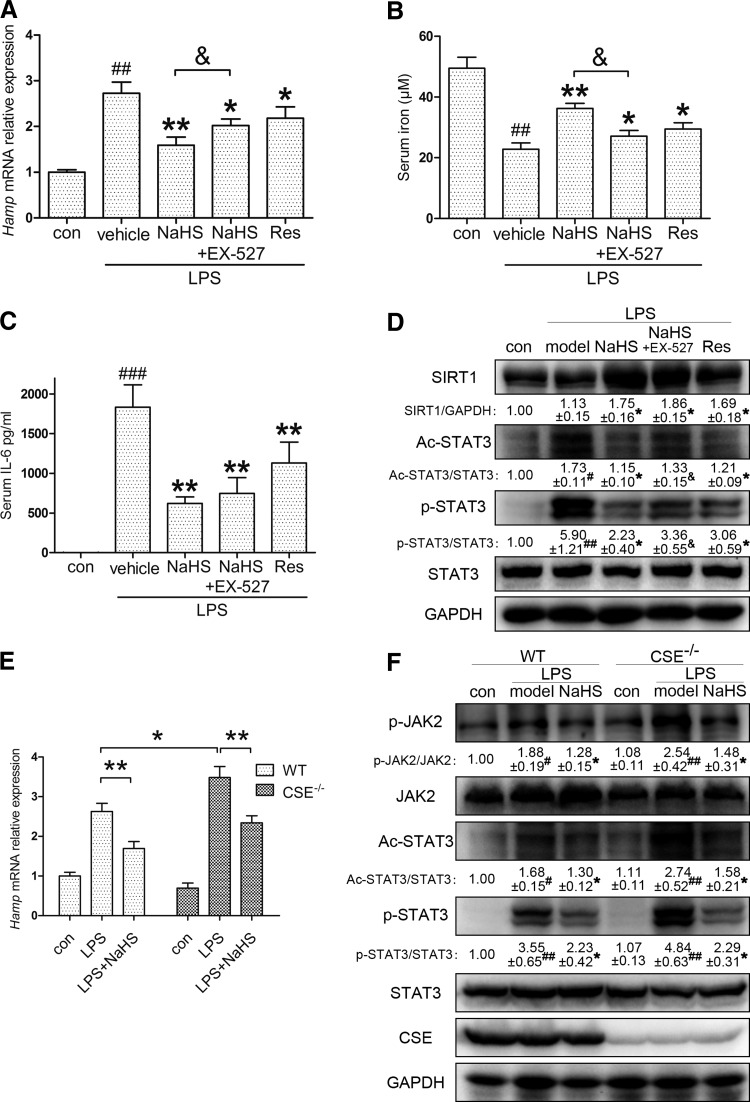
FIG. 6.
Suppressive effect of H2S on inflammatory hepcidin is diminished by SIRT1 inhibition and CSE knockout in vivo. (A) EX-527 (10 mg/kg) partially abrogated the attenuation of LPS (0.5 mg/kg)-induced Hamp expression by NaHS (6 mg/kg) in C57BL/6 mice. Resveratrol (10 mg/kg) also suppressed inflammatory Hamp induction (n=8). (B–D) Consistent results were demonstrated with serum iron and IL-6, as well as hepatic SIRT1, ac-STAT3, and p-STAT3 (n=8). (E) No significant change was observed in basal hepcidin levels after knocking out CSE. Compared with WT, CSE knockout (CSE−/−) mice were more susceptible to LPS challenge (0.5 mg/kg), whereas NaHS (6 mg/kg) successfully reversed the intense Hamp induction in the liver (n=6–8). (F) Representative immunoblots indicated that CSE deficiency exacerbated LPS-induced JAK2/STAT3 activation, which was rescued by NaHS (n=6–8). GAPDH served as the loading control. Representative immunoblots are presented with the results of densitometry analysis. Data are presented as the mean±SEM of three individual experiments. #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, and ###p<0.001 compared with the control group; *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared with the LPS group unless indicated; &p<0.05. WT, wild-type.