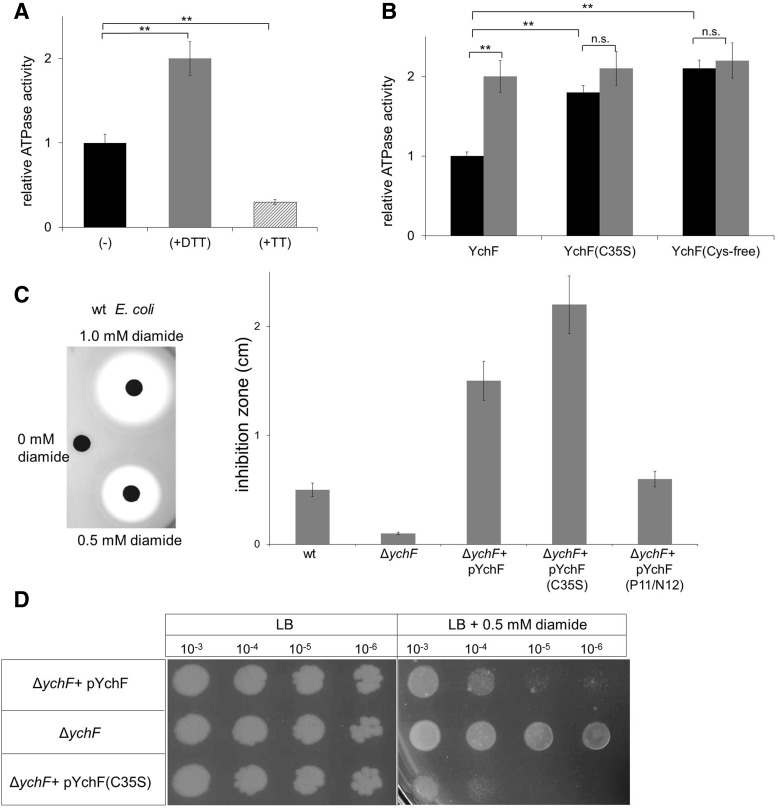
FIG. 4.
Dimerization of YchF inhibits its ATPase activity (A) The ATPase activity of purified wild-type YchF (black bar) was determined by measuring phosphate release of γ-33P-labeled ATP. When indicated, YchF was preincubated with either 10 mM DTT (gray bar) or 10 mM tetrathionate (TT) (hatched bar) for 5 min at room temperature before measuring the activity. A relative YchF activity of 1 corresponds to ∼0.35 nmol ATP/(min × mg protein). The relative ATPase activities shown are the mean ± SD (n > 3). **p < 0.01. (B) The ATPase activities of wild-type YchF, the YchF(C35S) mutant, and of the cysteine-free YchF mutant were determined without (black bars) or after preincubation with 10 mM DTT (gray bars). A relative YchF activity of 1 corresponds to ∼0.35 nmol ATP/(min × mg protein). The relative ATPase activities shown are the mean ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01; n.s. not significant. (C) E. coli strains were adjusted to an optical density of 0.5, mixed with Top agar, and poured on LB Plates. Filter discs were soaked with different diamide concentrations and placed on these plates. Inhibition zones were quantified after ∼5 h of growth and the results for wild-type E. coli are shown (left panel). Quantification of two independent experiments in the presence of 0.5 mM diamide (right panel). pYchF(P11/N12) corresponds to an ATPase-deficient YchF derivative. (D) The indicated E. coli strains were grown overnight on liquid LB medium without antibiotics and adjusted to an optical density of 1.0 before serial dilution. Dilutions were then spotted onto LB plates or LB plates containing 0.5 mM diamide. Plates were incubated at 37°C and analyzed after ∼12 h of growth.