Fig. 3.
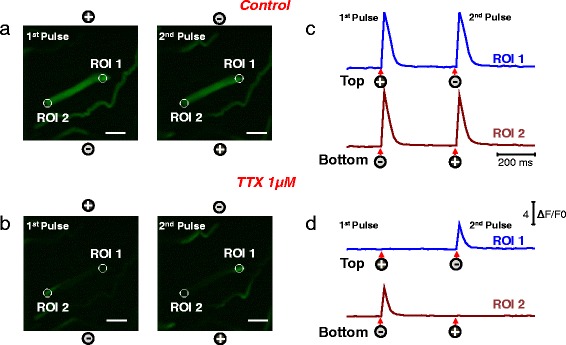
Myofibers exhibiting UNI responses under control conditions exhibit local Ca2+ transients (ALT responses) when treated with TTX. Myofibers with uniform responses were loaded with rhod-2, and their Ca2+ responses to electrical stimulation were recorded before and after the addition of TTX, a voltage-dependent Na+ channel blocker. Spatio-temporal properties of depolarization-induced rhod-2 Ca2+ transients in a myofiber that exhibited uniform responses in a physiological recording solution (a UNI) and ALT responses after treatment with TTX (b). Rhod-2 signals were imaged and analyzed as in Fig. 1 (see video in Additional file 4 for the entire time series). Scale bars in a–b are 100 μm. UNI myofibers exhibit a global Ca2+ transient in response to pulses of alternate polarity; however, the addition of TTX “converts” UNI myofibers into ALT myofibers that display only local non-propagated Ca2+ transients in response to pulses of alternate polarity, as the ALT myofibers described in Fig. 1b. The polarity signs indicate the location of the electrodes and their polarity for each stimulus. c, d show the time course of the rhod-2 fluorescence measured at the ends of the myofibers. Circles labeled as regions of interest (ROI) ROI 1 (myofiber’s upper end, blue trace) and ROI 2 (myofiber’s lower end, dark red trace) show the locations used to measure the time course of the rhod-2 fluorescence. Arrows and signs under the traces indicate both the polarity and the time when the pulses where applied. Vertical scale: ΔF/F0 = 4; horizontal scale: time 200 ms
