Fig. 6.
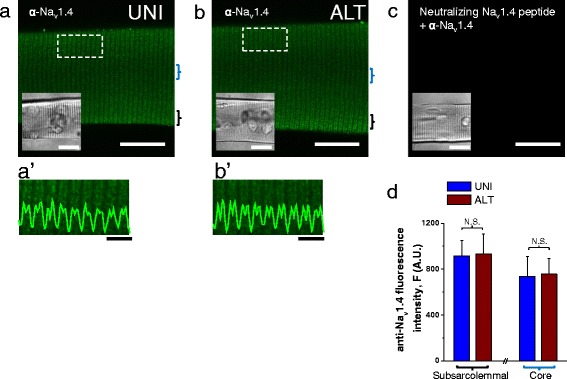
Nav1.4 sodium channel localization in UNI and ALT myofibers. Exemplar confocal images of UNI (a) and ALT (b) myofibers labeled with antibody to the intracellular II-III loop of Nav1.4. UNI and ALT fibers were identified using field stimulation and their locations within any tested dish were saved using a computer-controlled and motorized microscope stage, and then subjected to immunostaining protocol. After immunostaining, the same computer-controlled stage was used to localize and image the previously stored locations of corresponding UNI and ALT myofibers and then confocal imaging was performed. In each case, images show single confocal slices through the middle of the myofibers. Scale bars in a–c are 100 μm. a'–b' panels are zoomed-in versions of boxed regions indicated in panels a and b. Traces inserted on a'–b' are averaged fluorescence profiles across the box, scale bars: 4 μm. In both a-a' and b-b', the immunofluorescent staining is localized to repeated transversely oriented bands whose general periodicity corresponded to that of T-tubules (see Fig. 2a, b). These images show that there are little, if any, differences in the immunolocalization of Nav1.4 channels between UNI and ALT myofiber types. c shows myofiber where the Nav1.4 antibody was preincubated with the Nav1.4 II-III loop neutralizing peptide before labeling. Insets in a-c are transmitted light images of myofibers shown in confocal images. d bar plot summarizing Nav1.4 channel staining intensity measured at the subsarcolemmal and core regions of UNI and ALT myofibers. N.S. Indicates P > 0.05 when compared with UNI control fibers, two-sample t test
