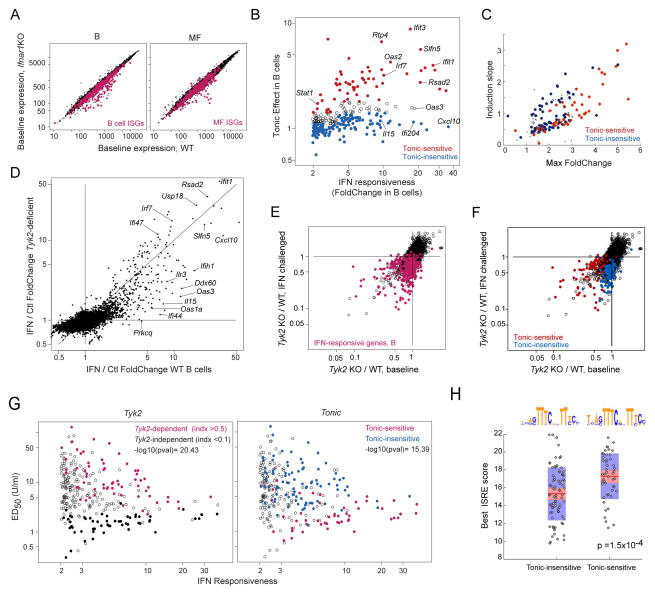
Fig. 2. Signal requirements for tonic and induced ISG expression in B cells.
(A). Comparison of B cell and macrophage profiles of WT or Ifnar1-deficient mice. Red: common ISGs per Fig. 1. (B) ISG response intensity (change 2 hrs after IFN) and dependence on tonic IFN signaling at baseline (Foldchange between untreated B cells, WT and Ifnar1-KO). (C) Positioning of “Tonic-hi” and “Tonic-lo” ISGs (per B) relative to response kinetics of Fig. 1F. (D) Foldchange/Foldchange plot comparing ISG induction in B cells from WT or Tyk2-deficient mice. (E) Expression ratios (Tyk2-deficient / WT) in resting or in IFN B cells. B cell ISGs in red. (F) As E, highlighting tonic-sensitive and tonic-insensitive (per B). (G) ISG response intensity vs ED50 (Fig. 1F), highlighting TYK2-dependency (left) or sensitivity to tonic signaling (right). (H) Max ISRE motif scores (JASPAR) in TSS and 5′ upstream regions of ISGs distinguished by sensitivity to tonic signaling; consensus sequence for each set, ignoring outliers, shown at top (Wilcoxon rank sum test p.vals). See Fig S2 and Tab. S1E.