FIGURE.
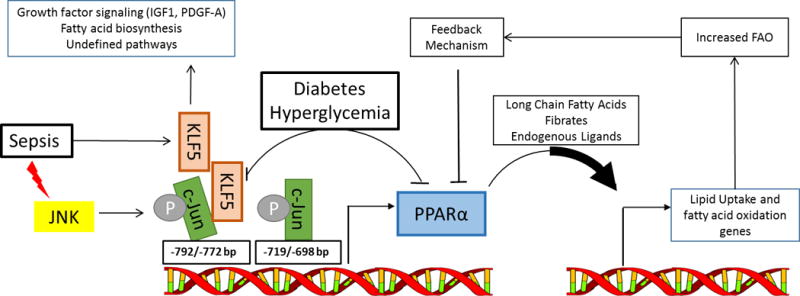
PPARα expression and fatty acid oxidation in the heart: proposed regulation by KLF5, sepsis and diabetes. PPARα level and the availability of its ligands regulate the expression of key proteins for fatty acids transport and oxidation (FAO) in the heart. Alterations in FAO act through feedback mechanisms to regulate PPARα expression and restore FAO to optimal levels. Deletion of KLF5 in the heart resulted in lower PPARα expression and decreased FAO. PPARα transcript levels are reduced in parallel to reduced KLF5 expression in early stage of diabetes, while in sepsis the activation of c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) phosphorylates c-Jun which binds to the PPARα promoter and prevents transcription of PPARα by KLF5. KLF5 has non-metabolic actions on the heart as well including effects on growth factor signaling and fatty acid biosynthesis in addition to other pathways suggested by microarray analysis of mouse hearts with cardiac-specific deletion of Klf5.
