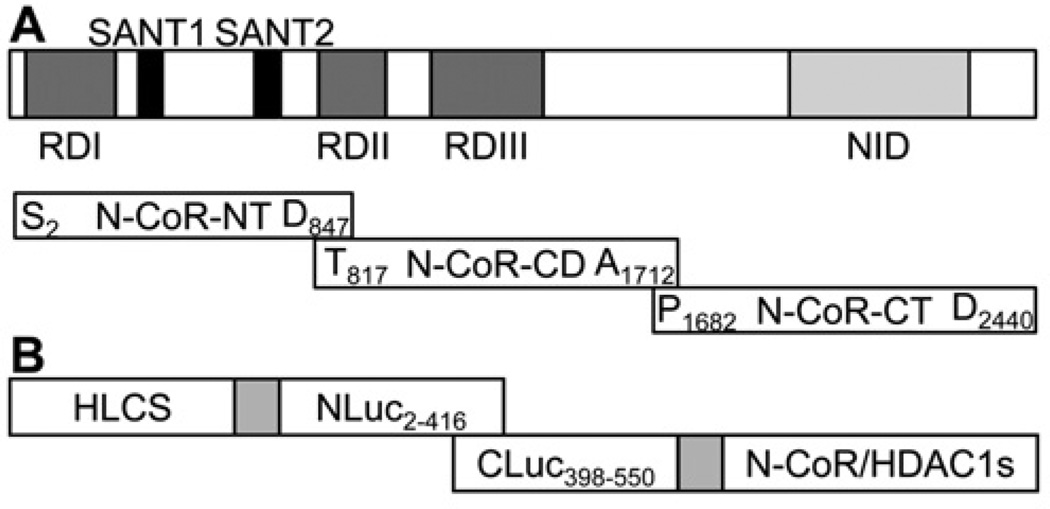
Figure 2. Schematic diagrams of domains in N-CoR and luciferase constructs used in the split luciferase complementation assays.
(A) The N-terminus of N-CoR contains transcriptional repression domains (RDs) responsible for the recruitment of additional components of the co-repressor complex such as HDAC, mSin3 and GPS2 (G-protein-pathway suppressor 2). A pair of potent repressor motifs known as SANT motifs (SWI3, ADA2, N-CoR and TFIIIB) is positioned between the repression domains. SANT motifs recruit HDAC3 and histones to the repressor complex in order to enhance HDAC3 activity. The C-terminus of N-CoR includes a nuclear receptor interaction domain (NID), which binds ligand-free nuclear receptors. In order to assign putative interactions with HLCS to distinct domains in N-CoR, three overlapping fragments of N-CoR were cloned, N-terminal domain (NT), central domain (CD) and C-terminal domain (CT). (B) In split luciferase complementation assays, N-terminal and C-terminal fragments are fused to interacting proteins. Physical interactions between the two proteins reconstitute luciferase activity.