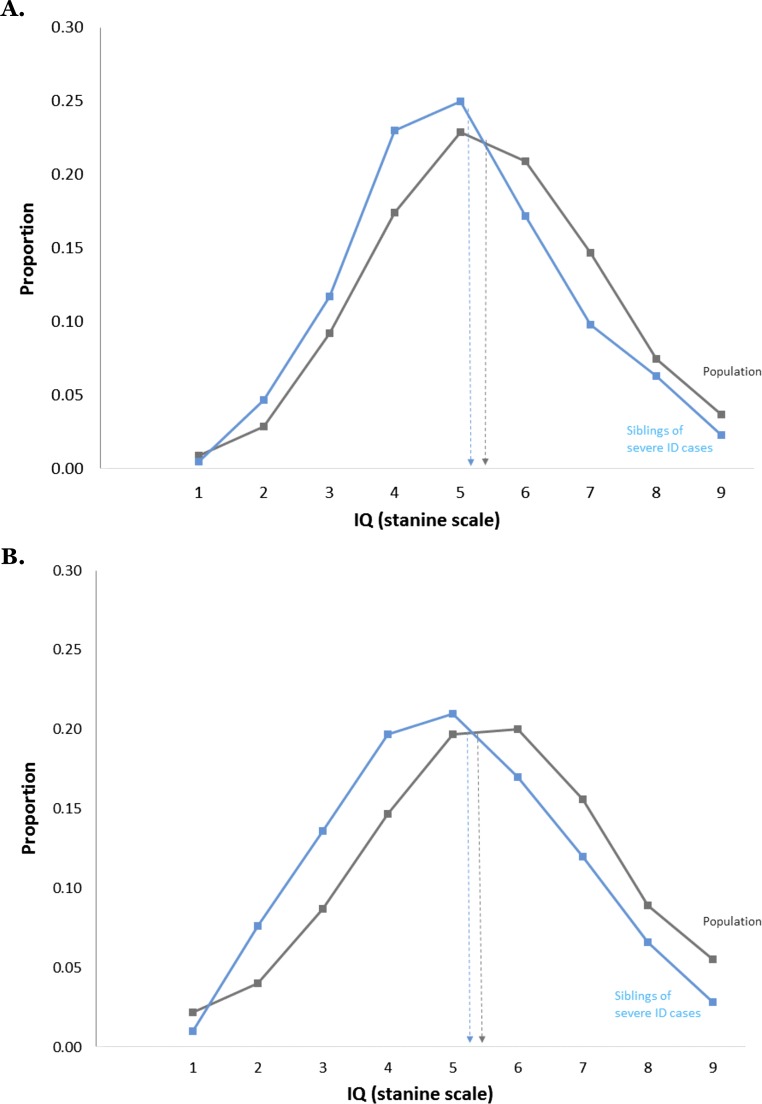
Fig. S2.
Severe ID is etiologically different from mild ID and normal variation in IQ in males and females. Siblings of persons with severe ID have IQs indistinguishable from the rest of the population. (A) Israeli results: distribution of IQ scores for females who have a female sibling diagnosed with severe ID (mean = 5.04, SD = 1.65, n = 256 pairs) and the female population distribution (mean = 5.39, SD = 1.68, n = 120,973 pairs). (B) Israeli results for opposite-sex (female–male and male–female) siblings with a sibling diagnosed with severe ID (mean = 5.02, SD = 1.81, n = 1,223 pairs) and for the population (mean = 5.46, SD = 1.87, n = 250,301 pairs). These results are from Israel only because only male siblings and twins are available for the Swedish sample.