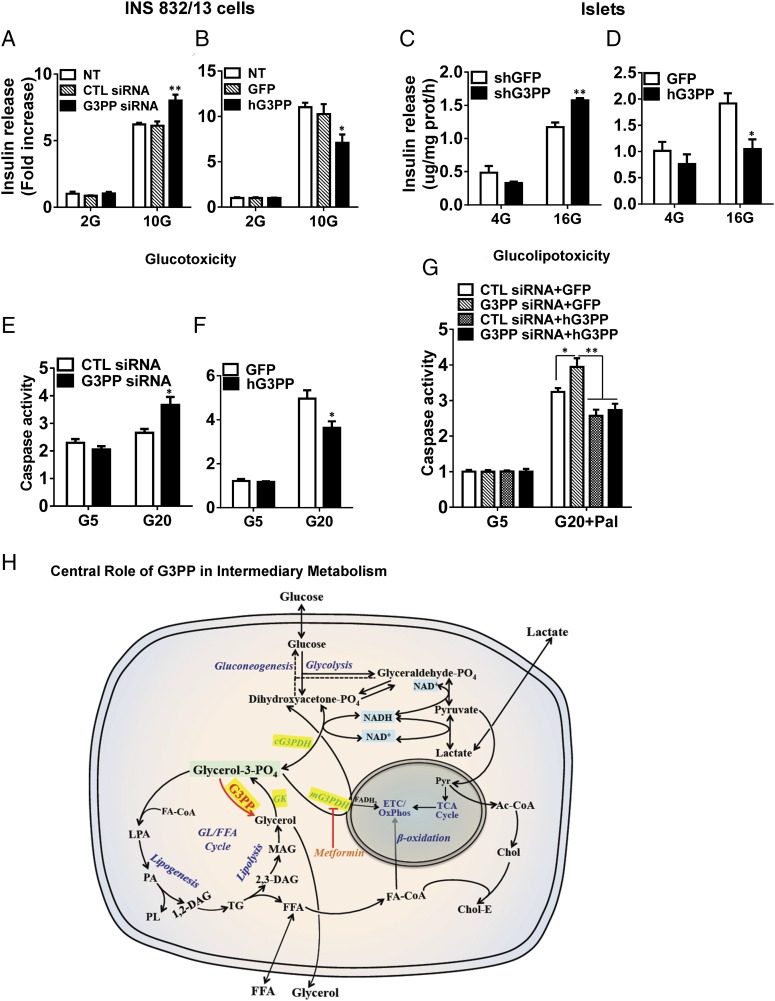
Fig. 2.
Activity of G3PP controls GSIS, glucotoxicity, and glucolipotoxicity in β-cells. (A and B) Insulin secretion in INS832/13 cells at 2 mM and 10 mM glucose after G3PP knockdown (A) or hG3PP overexpression (B). CTL, control; NT, not transfected (mean ± SEM of three experiments with triplicate observations; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding controls). (C and D) Insulin secretion in isolated rat islet cells at 4 mM and 16 mM glucose after G3PP knockdown (C) or hG3PP overexpression (D) (mean ± SEM of three experiments with triplicate observations; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding controls). (E and F) Glucose-induced apoptosis (glucotoxicity) in INS832/13 cells after G3PP knockdown for 24 h (E) or hG3PP overexpression for 72 h (F). Caspase activity was determined in cells exposed to 5 mM and 20 mM glucose (mean ± SEM of three experiments with triplicate observations; *P < 0.05 vs. corresponding controls). (G) Glucose plus palmitate-induced apoptosis (glucolipotoxicity) in INS832/13 cells after G3PP RNAi knockdown with or without rescue by hG3PP overexpression. Controls were set up with control siRNA for knockdown and GFP for overexpression. Glucolipotoxicity was induced for 48 h by 20 mM glucose plus 0.3 mM palmitate and compared with 5 mM glucose value (mean ± SEM of three experiments with triplicate observations; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding controls; control siRNA, shG3PP, and GFP). (H) Scheme illustrating the central role of G3PP in intermediary metabolism. Gro3P formed from glucose metabolism or by the phosphorylation of lipolysis-derived glycerol is at the crossroads of intermediary metabolism. G3PP, by controlling Gro3P, plays a central role in the regulation of intermediary and energy metabolism and cellular redox. Ac-CoA, acetyl-CoA; cG3PDH, cytosolic G3PDH; Chol, free cholesterol; Chol-E, cholesterol ester; ETC, electron transport chain; FA-CoA, fatty acyl-CoA; GK, glycerokinase; GL/FFA, glycerolipid/FFA; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; mG3PDH, mitochondrial G3PDH; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation; PA, phosphatidic acid; PL, phospholipids; Pyr, pyruvate.