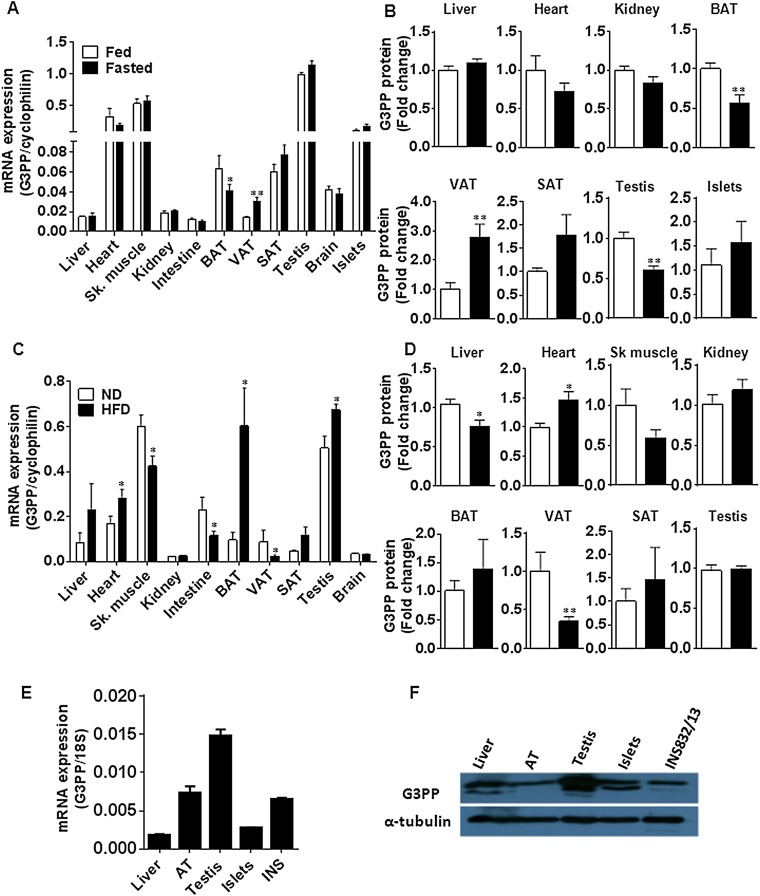
Fig. S2.
Regulation of G3PP expression by nutritional status in mice and tissue distribution of G3PP in rats. (A and B) G3PP expression in the fed and fasted states in various tissues. Male mice were fed normal chow diet and one group was starved overnight before they were euthanized. Tissues were isolated and G3PP expression was measured. (A) G3PP mRNA levels normalized to corresponding tissue cyclophilin mRNA. (B) G3PP protein expression in different tissues assessed by Western blots and densitometry. G3PP protein levels were normalized to corresponding tissue levels of β-actin or α-tubulin and expressed as fold change in expression (means ± SEM; n = 6; *P < 0.05). (C and D) Effect of HFD on G3PP expression in various tissues. Male mice were fed normal diet (ND) or HFD (60% calories from fat) for 8 wk and then killed, and tissues were collected for the assessment of G3PP expression. (C) G3PP mRNA levels. (D) G3PP protein levels (means ± SEM; n = 5–10; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). SAT, s.c. adipose tissue; Sk. muscle, skeletal muscle; VAT, visceral adipose tissue. (E) Expression of G3PP mRNA in normal Wistar rat tissues and in the rat β-cell line IN832/13 (means ± SEM; n = 4). (F) Expression of G3PP protein in different rat tissues. Representative blot of three experiments.